If you've ever seen a dump truck pour a load of sand, you've watched the sand as it formed a conical pile behind the truck. Why conical? Because the sand can only support a fraction of its weight. As more is poured on, the pile collapses under its own weight.
Now imagine what would happen to the pile of sand if you walked
on it. It would collapse even more. Right? What if you drove
a tractor on it?
It's easy to perceive a canal bank as solid, but actually
it is just like the pile of sand. If you add too much additional
weight, the bank will collapse. If you and your tractor are
unlucky enough to be that extra weight, it could be the last
ride you take.
Every year, farmers die when they drive a tractor too close
to an embankment, and the collapse of the bank leads to an
overturn. It happens quickly and with tremendous force, but
it can be avoided.
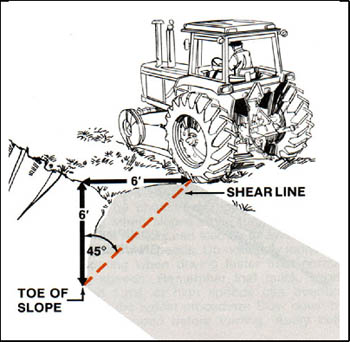
Equipment needs to be kept behind the shear line of the soil
and embankment. The minimum distance recommended for operating
machinery near embankments is a 1:1 ratio to the depth of
the embankment. In other words, the tractor should be no closer
to the edge than the depth of the embankment (Figure 1). Following
this recommendation prevents bank collapse that can cause
tractors to overturn thus crushing operators or drowning them
in canals. This distance increases with adverse soil conditions
such as sandy or wet soil.
In some cases, it may be a good idea to move field roads farther
from canals and ditches so that tractors are not forced to
travel in the danger zone.
Figure 1. Stay on the safe side of the shear line and
prevent bank collapse and tractor overturns

For More Information
For more information about tractor safety, visit the Florida
AgSafe Network Web site:
http://www.flagsafe.ufl.edu
The following publications are available at your county Extension
office and at the EDIS Web site, <http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu>.
(IFAS Publication Numbers are in parentheses after the titles.
The second set of parentheses contains the Web address at
which the publication can be viewed.)
Publication #: AE305
1.
This document is
AE305
,one
of a series of the Agricultural and Biological Engineering
Department, Florida Cooperative Extension Service, Institute
of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida.
Supported in part by the NIOSH Deep-South Center for Occupational
Health and Safety, University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida.
First published September 2001. Please visit the EDIS Web
site at http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu
2. Carol J. Lehtola, assistant professor, Department of Agricultural
and Biological Engineering, and Extension Agricultural Safety
Specialist, and Charles M. Brown, Assistant Coordinator for
Agricultural Safety and Health, Institute of Food and Agricultural
Sciences, University of Florida, Gainesville, 32611.
The Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences is an equal opportunity/affirmative action employer authorized to provide research, educational information and other services only to individuals and institutions that function without regard to race, color, sex, age, handicap, or national origin. For information on obtaining other extension publications, contact your county Cooperative Extension Service office. Florida Cooperative Extension Service/Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences/University of Florida/Christine Taylor Waddill, Dean.
Disclaimer and Reproduction Information: Information in NASD does not represent NIOSH policy. Information included in NASD appears by permission of the author and/or copyright holder. More