Contents
Cholinesterase Basics 1
Patricia Boiko
Goal: To provide information and resources to growers and managers.
Schedule Growers/Manager Breakout
1:30- 2:00 Cholinesterase basics Patricia Boiko
2:00- 2:30 Cholinesterase monitoring rules John Furman
2:30- 3:00 Cholinesterase testing and informed consent/dissent John Furman
3:00- 3:15 Break- Handlers interact with growers and health care providers
3:15- 3:35 Practicalities of the rule Dr. Todd Denny
3:35- 4:00 Grower experiences a monitoring programs
The Rule
Employers must provide cholinesterase monitoring
- Baseline plasma and rbc cholinesterase
- Follow-up plasma and rbc level
- To OP and Carbamate pesticide handlers
- Who handle for 50 hours or more in a thirty day
period for 2004, 30 hours in 2005
Medical Providers Role
According to WAC 296-307-148 Licensed
Health Care Providers must:
-
Discuss the risks and benefits of handler participation
in cholinesterase monitoring
- Obtain a signed declination if the handler chooses not
to participate
- Provide and interpret baseline and periodic testing of
blood cholinesterase levels
- Provide other written occupational health
recommendations as indicated.
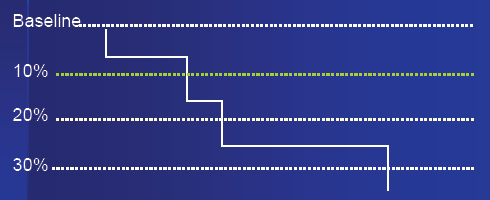
Cholinesterase Basics: >20% Depression From Baseline
Understand
- Basic science of cholinesterase and cholinesterase
inhibiting pesticides
- Everything about monitoring
- Testing methods
- Responses to a positive test: Cholinesterase depression
false positives
- Quality assurance evaluation
The Rule
- Listen for
- Which pesticides
- Which workers
- What is the responsibility of
growers/managers
Handler Consent
- Rule says the handler must sign a
written declination statement of which a
copy goes to the grower
- WHAT DOES THIS MEAN FOR YOU??
Reporting Requirements and Poisoning
- Pesticide-related illness
-
Reportable condition to the Washington State Department of Health (WAC 246-10)
- All types pesticide-related cases must be reported
- Including skin, eye injuries, systemic poisonings, suicides, homicides,
- Home and occupational exposures.
Why is ChE Testing Useful?
- ChE reflects the substance on its target
- Integrates exposure over time
- The test is available
- Blood tests are available
BUT!
- Good lab methods needed
- Interpretation and timing important
- Sample handling important
Objective
To understand the basic biology of cholinesterase and cholinesterase inhibiting pesticides.
Biology of Cholinesterase
-
Present from paramecia to sapiens
- Very Fast enzyme
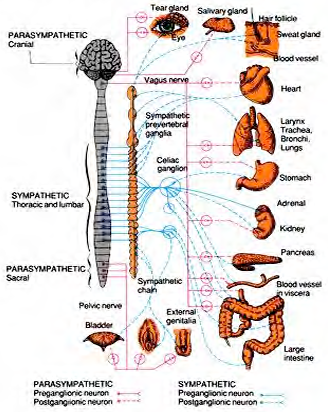
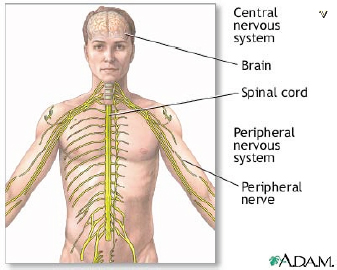
Ubiquitous in the human body
- Critical for many nervous system
functions

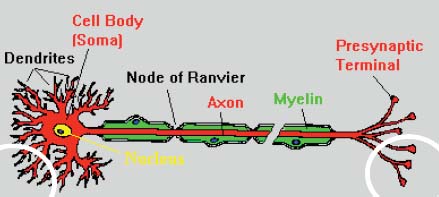
Cholinesterase Enzyme
-
Produced in tissues and blood
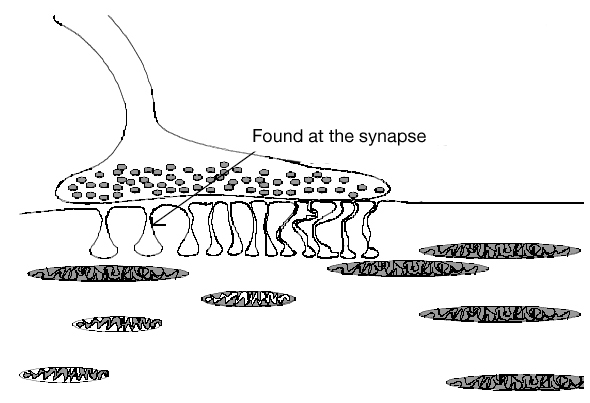
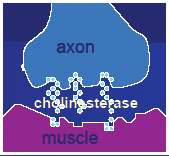
- Hydrolyzes acetylcholine: A key neurotransmitter
- Present in the autonomic, central and peripheral nervous systems
Two Different Kinds of ChE enzymes
-Some behaviors in common
-
Plasma Cholinesterase
- Butyrylcholinesterase,
pseudocholinesterase, PChE, or just
cholinesterase and ChE
- RBC Cholinesterase
- True cholinesterase,
acetylcholinesterase, or AChE
Plasma ChE
- Floats freely in plasma
- Made by liver
- Rapid recovery from depression
- Rapid replacement by new synthesis
- Liver disease may affect levels
- Sensitive to most ChE inhibitor
pesticide exposures
Red Blood Cell Cholinesterase
-
Bound to red blood cells
- Made at the same time as the Rbc's
- Recovery from depression 0.8%/day
- Slower to depress, slower to recover
- Low RBC count may cause lower levels
- Identical to neuronal ChE
What Cholinesterase Does: Physiologically