
Exposure to noise above 85 dB can cause hearing loss and tinnitus.
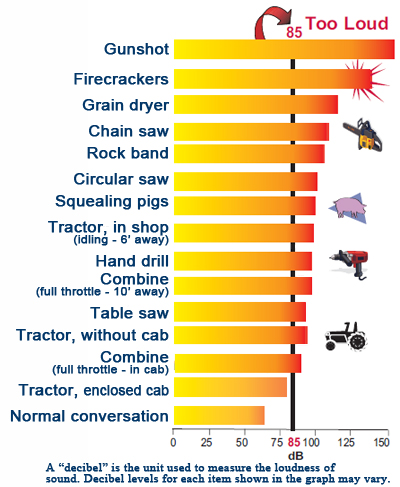
If you need to raise your voice to be heard an arm’s length away,
the noise is probably loud enough to damage your hearing.
Hearing protection is available from many sources including on the internet and in home improvement and farm stores.
Remember, size matters! Not every earplug fits every ear. You may even need a different size for each ear. If you can’t get at least half of the plug into the ear canal, or if it can’t expand enough to stay firmly seated, you need a different size.
Earmuffs may work well for you. These are often worn during hunting and shooting. Some have a built-in radio as well as electronic circuits to limit the noise. They allow you to listen to your favorite sports or music. They are usually easy to fit and convenient to put on and take off. They can also make great gifts. However, if you wear glasses, earrings or have facial hair, ear plugs may be a better choice to ensure proper fit and sound reduction.

Replace your ear plugs or the seals of your ear muffs when they look worn or feel different.
Size Matters To fit properly, a formable plug should be inserted so that most of the plug fits into the ear canal. While many formable plugs are "one size fits most," different sizes are available. If you can't get at least half of the plug into the ear canal, or if the plug can't expland enough to stay firmly seated, you need a different size.
1) ROLL the formable plug between your thumb and forefinder(s) to compress it into a small, smooth, round cylinder.
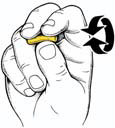
2) REACH over top of your head and pull up or back on the top of your ear. This straightens out your ear canal so the plugs can go in far enough.
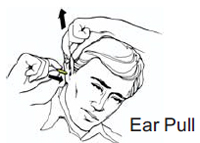
3) INSERT tightly rolled plug into straightened ear canal.
4) HOLD the ear plug in place for a few seconds after inserting to give it time to expand and seat itself in the ear canal.
Remember, the plug must be rolled down tightly before you try to insert it into your ear canal. You shouldn't try to push a formable plug into your ear if you have not rolled it tight enough.
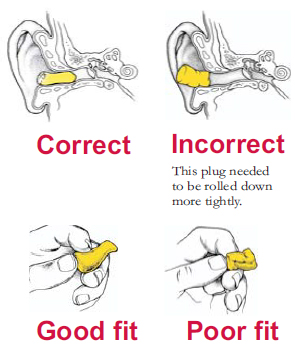
When you remove the plug, check to make sure there is a slight bend. (See the drawings above.) The bend means the earplug was inserted deeply enough to reach the bend in the ear canal. There should be no creases in the earplug.
Although considered disposable, formable plugs can be washed and used repeatedly.
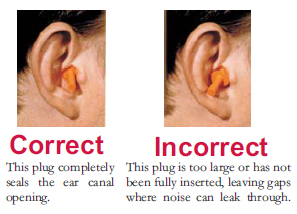
Premolded plugs may come in different sizes or as "one size fits most." Try out different sizes or as "one size fits most." Try out different sizes to find the ear plug that fits you best.
1) REACH over top of your head and pull up or back on the top of your ear. This straightens out your ear canal so the plugs can go in far enough.

2) INSERT premolded plug into straightened ear canal.
With a premolded plug, you can perform the "tug test." To do this, gently pull in and out on the stem of the earplug. As you do so, you should feel pressure changes in your canal to confirm you have a good fit. Do not pull hard enough to break the seal.
Premolded plugs are reusable. Most can be easily washed using mild soap. Make sure they are completely dry before storing them in their case or using them in your ear. Using wet plugs can irritate ear canals.
 Canal caps are formable or premolded earplugs attached to a headband. Depending on the design, headbands may be worn over the head, behind the neck or under the chin. The headband allows canal caps to be hung around the neck when not being used. This makes them convenient to use when noise is not constant and you are taking your earplugs in and out frequently. Fitting and using canal caps is otherwise similar to fitting and using formable and premolded plugs.
Canal caps are formable or premolded earplugs attached to a headband. Depending on the design, headbands may be worn over the head, behind the neck or under the chin. The headband allows canal caps to be hung around the neck when not being used. This makes them convenient to use when noise is not constant and you are taking your earplugs in and out frequently. Fitting and using canal caps is otherwise similar to fitting and using formable and premolded plugs.
If you are around noise at work, at home or doing the things that you enjoy, you need to protect your ears. If you don't, you can expect to develop permanent hearing loss. You may also develop a permanent ringing, buzzing or roaring in your ears known as Tinnitus.
For additional copies, questions, or comments related to this brochure, e-mail farm.noise@cdc.gov
Credits: The graphics used to illustrate fitting ear plugs were provided,
courtesy of Elliott Berger, Senior Scientist, Auditory Research E-A-R/Aearo Company
To receive other NIOSH documents or for more information about occupational safety and health topics, contact:
1–800–CDC–INFO (1–800–232–4636)
TTY: 1–888–232–6348
E-mail: cdcinfo@cdc.gov or visit the NIOSH Web site at www.cdc.gov/niosh.
For a monthly update on news at NIOSH, subscribe to NIOSH eNews by visiting www.cdc.gov/niosh/eNews.
DHHS –( NIOSH) Publication No. 2007–176
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health

Publication #: DHHS –( NIOSH) Publication No. 2007–176
Disclaimer and Reproduction Information: Information in NASD does not represent NIOSH policy. Information included in NASD appears by permission of the author and/or copyright holder. More