Introduction
What's Inside?
Lesson 1 Take Control of Your Own Safety
Lesson 2 Prepare for Safe Operation
Lesson 3 Avoid Being Caught in the Chipper
Lesson 4 Avoid Being Struck by Equipment's Hood
Lesson 5 Environmental Hazards
Conclusion
Quiz Yourself Solutions
This booklet teaches important safety practices to be followed when operating a chipper/shredder.
Safety tips, along with real accident reports, have been combined in order to give you a better understanding of the risks of incorrectly operating equipment as well as working in unsafe environments.
Use this booklet in conjunction with hands-on safety training and the equipment operator's manual.
- Name the most common types of accidents involving wood chipper/shredders.
- Interpret the meaning of common warning signs and labels.
- Identify appropriate protective equipment.
You can be seriously injured or killed if you incorrectly operate a chipper/shredder. The most commonly reported causes of serious accidents are:
- Being Caught in Moving Parts
You can be seriously injured or killed if you are caught in the
equipment's moving parts.
Accident Report
Employee Killed in Chipper |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 300492832
An employee was chipping branches when the chipper became jammed. He tried to unjam the machine and was caught in the infeed roller and chopped to death by the blades.
 Never reach in to a running chipper/shredder. Never reach in to a running chipper/shredder.
|
- Struck by Chipper/Shredder's Hood
You can be seriously injured or killed if you open or close the hood on a running chipper/shredder.
Accident Report
Employee Struck by Chipper Hood |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 124829318
An employee attempted to close the hood on a running chipper. The hood struck some moving parts and hit the employee in the chin, flinging him backward. His head hit the pavement and he was killed.
 Never open or close the hood of a running chipper/shredder. Never open or close the hood of a running chipper/shredder.
|
Safe work habits are important. Here are three important actions you can take to be safe on the job site.
- Learn all you can.
To prevent accidents with wood chippers/shredders, read and
follow directions in the equipment operator's manual. Pay attention to safety instructions in the manual and to warning labels you see on the equipment. If you have questions, stop and ask your supervisor before you continue.
- Concentrate on working safely.
Sometimes you may be tempted to take risky shortcuts.
Remember that an accident can leave you permanently injured
or cut your life short. For your safety and the safety of those
around you, do not take unnecessary risks. No deadline is so
pressing you can't take the time to do your work safely.
- Additional Precautions
Do not operate machinery if you are tired or have taken drugs or
alcohol. If you are on medication, discuss with your doctor or
pharmacist if you are capable of safely operating machinery.
Manufacturers put important safety messages on each piece of equipment and in the operator's manual. It is critical to read, understand and follow all safety messages.
 The triangle shape is the symbol for caution. The exclamation mark in the center means Pay Attention. In some instances, the triangle-shaped sign will show a picture. Other times, words explain why the sign is used.
The triangle shape is the symbol for caution. The exclamation mark in the center means Pay Attention. In some instances, the triangle-shaped sign will show a picture. Other times, words explain why the sign is used.
Many safety messages use the words Caution, Warning and Danger to get your attention. Following are safety messages and their meanings. Each of these signs will have a written message, and perhaps a picture, about an unsafe condition.
CAUTION means you need to be careful. Follow the directions on the sign or you could get hurt.
WARNING is more serious and means you need to follow the directions on the sign or you could be badly hurt or killed.

DANGER is the most serious safety message. If you don't follow the directions, you will be seriously injured or killed.

Images displayed in the caution, warning and danger boxes have been recreated from images taken with permission from ASAE S441.4, FEB04, Safety Signs.
Certain equipment is necessary to protect your body from materials thrown from the chipper/shredder and to avoid being caught in the equipment's moving parts.
When operating a chipper/shredder, you should wear:
Close-fitting clothes and no jewelry.
Loose shirt sleeves, pant legs or jewelry can catch in the equipment's moving parts, resulting in injury. Do not wear gloves with loose cuffs. Pull back long hair.
Long pants and sturdy, non-slip boots.
Wear long pants, without cuffs, to protect your legs from objects that could be thrown from the chipper. Sturdy, non-slip boots will help you keep a firm footing on the ground and reduce the risk of slipping and falling into the chipper/shredder.
Safety glasses.
Wear safety glasses to protect your vision.
Hard hat.
Wear a hard hat to protect your head from material that may be kicked out of the machine.
Hearing protection.
Over time, you will lose your hearing if you are exposed to loud noises without protection.
Two common types of hearing protection are muffs and plugs. Ear muffs should seal around your ears to properly muffle loud noises. Wash reusable ear plugs with warm, soapy water after each use in order to prevent infection. Discard disposable ear plugs after each use.
When to Wear Hearing Protection
OSHA Standard 1910.95 (i) (l) requires hearing protection to be worn when sound levels exceed certain limits (generally, a daily average of 85 or 90 decibels, depending on the circumstances). These levels can be measured with a sound level meter. A hearing conservation program requiring hearing tests and other precautions may also be necessary. Check with the equipment operator's manual, as well as your supervisor, for suggestions on hearing protection for each piece of equipment as well as instructions on how to wear it properly.
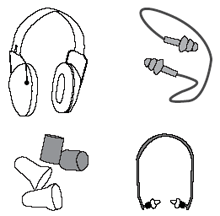
Hearing Protection Rules of Thumb
Hearing protection may be needed if:
- You have to raise your voice significantly to be heard by someone three feet away.
- After leaving a noisy area, your ears feel plugged or you hear a mild ringing or whooshing noise that goes away after an hour or two.
- When you start your car in the morning, the radio is so loud from the evening before that you have to turn it down.
This logger's style safety helmet can also be used while operating a chipper/ shredder. It contains a hard hat, hearing and face protection in one piece.
Choose the correct answer.
For answers, click here.
- What are the two most commonly reported causes of serious injury and death from operating wood chippers?
- Being caught in moving parts & being struck by the hood
- Being struck by lightning & heat stroke
- Being struck by debris & burns
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
a. Danger
b. Hard hat
c. Alcohol
d. Triangle
- Do not operate machinery if you are under the influence of drugs or _________.
- The __________ shape is the symbol for caution.
- A __________ should be worn at all times when operating a chipper/shredder.
- _________ is the most serious safety message.
- Indicate features to be inspected before operation.
- Recognize safe operating procedures.
- Identify safe transportation and traffic guidelines.
Safety starts before the engine. Thoroughly inspect the chipper before beginning work each shift. Use the following checklist as a guide. Alert your supervisor if you find anything wrong during your pre-start inspection.
Machine Placement
Place the machine on a level surface that is not concrete, paved or gravel. Operating on these surfaces can cause thrown material to ricochet and injure or kill the operator or bystanders. Also keep other workers from falling into the chipper/shredder by ensuring the location of the machine is not directly in front of or below where other employees are working.
Accident Report
Employee Falls When Rope Becomes Caught in Chipper |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 112887237
An employee was removing a tree when the tail section of the rope to which he was attached became entangled in the chipper located on the ground below. The employee fell approximately fifty feet and died.
 Position equipment away from other workers. Position equipment away from other workers.
|
Safety Decals
Ensure that all safety decals on the machine are legible. Replace any that cannot be read. Contact the chipper's manufacturer to order new decals. Contact information can be found in the operator's manual.
Missing or Damaged Guards
Guards and shields protect you from moving parts. Check the operator's manual for the location of guards and safety shields.
Accident Report
Operator Pulled Into Chipper |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 110902368
An employee was operating a wood chipper without all guards in place. He became caught in the rollers and was pulled through the chipper and killed.
 Never operate equipment without all guards in place. Never operate equipment without all guards in place.
|
Hood
Ensure the hood, enclosing the chipper/shredder's knives, is closed and latched before operating. Also, check for loose or missing pins in the hood latch as well as cracked or worn hinges. If the hood is not properly secured, it could fly off and seriously injure or kill you. The chipper/shredder should never be operated with the hood open.
Accident Report
Hood Strikes Employee in Head |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 114119498
An employee was trying to open or close the chipper hood when it was struck by the disc. As the disc hit the hood, the hood was flung off its hinge, striking the employee in the head and killing him. Two latch pins and three mounting bolts were found after the accident had occurred. They had been removed prior to the accident.
 Always inspect equipment for broken or missing parts, before operating. Always inspect equipment for broken or missing parts, before operating.
|
Cutting Chamber
Ensure the cutting chamber is free of foreign objects or other debris such as accumulated wood. Wood and foreign objects can be thrown from the chipper at high rates of speed.
Fluid Leaks
Fluid leaks can cause fires and breakdowns. Report signs of leaking fluid to your supervisor immediately.
Power Take-Off (PTO)
Check to make sure the PTO shaft is fitted correctly with a suitable guard. Also, check the operator's manual to ensure the PTO speed is suitable for the machine.
|
| |
| Machine Placement |
 |
On level surface? |
 |
Not on paved, concrete or gravel surface? |
| |
|
| Safety Decals |
 |
Legible? |
| |
|
| Guards |
 |
All guards in place? |
 |
No sign of damaged guards? |
| |
|
| Hood |
 |
Closed? |
 |
Latched? |
 |
Pins in place? |
 |
Hinges not damaged? |
| |
|
| Cutting Chamber |
 |
Free of foreign objects? |
 |
Free of wood and other debris? |
| |
|
| Fluid Leaks |
 |
No sign of fluid leaks? |
| |
|
| PTO |
 |
Shaft fitted with suitable guard? |
 |
Speed suitable for machine? |
- Always work in groups of two or more. Be aware at all times of the location of coworkers.
- Make sure someone knows your plans: where you are going, what you are doing and when you are going to be back.
- If you have any severe allergies (such as bee sting), make sure someone you are working with knows about the allergy and what to do in the event of an allergic reaction.
| Those with severe allergies to insect stings should consult a physician about carrying a prescription medical kit. The kit contains medicine and instructions to be used if the person is stung. If the kit is used, the victim still must receive medical attention. Call for help or take them to the nearest hospital. |
- Start the chipper/shredder at the lowest possible speed and listen for any noise or vibration that could indicate loose or broken parts. If heard, turn off the machine.
- Be aware at all times of the location of coworkers. Keep all others out of the area.
- Check the operator's manual for additional procedures.
PTO
Additional precautions for PTO-driven models:
- Ensure the PTO is hitched securely and level according to the operator's manual.
- Put the tractor in neutral and set the parking brake.
- Start the tractor engine, engage PTO clutch and then increase speed to recommended RPM.
- Disconnect the power supply and remove key. You can tell the machine has stopped when no noise or vibration is heard.
- Check the operator's manual for additional procedures.
Accident Report
Chipper Hood Strikes Employee in Stomach |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 119960789
An employee turned off a chipper's motor, but did not wait the recommended (by the manufacturer) five minutes before opening the hood to allow the parts to come to a stop. When the employee opened the hood, the flywheel struck the edge of the hood and flung it into the employee's stomach. His intestines were bruised and had to be partially removed.
 Wait for all moving parts to come to a Wait for all moving parts to come to a
complete stop before opening the hood.
|
Gasoline and other fuels are flammable. Following safe fueling procedures will help reduce the risk of fuel ignition.
- Always shut off the engine and wait at least 5 minutes for the engine to cool before refueling.
- Use only approved fuel containers and store in a well ventilated area, away from direct sunlight.
- Never smoke or have an open flame near fuel.
- Touch the fuel nozzle to the chipper/shredder before opening the fuel cap to reduce the chance that a static spark will ignite the fuel. Keep the nozzle in contact with the filler neck while fueling. Replace the cap as soon as you are finished.
- Use a funnel or non-spill nozzle when fueling to reduce spillage.
- Wipe up all spills immediately, before starting the engine.
- Never clean your hands or tools with gasoline. Use a nonflammable solvent instead.
- Set the container on the ground.
- Touch the fuel nozzle to the container before opening the fuel cap so that any static spark will not ignite vapors.
- Keep the nozzle in contact with the container while filling.
- Don't fill to the brim. Leave room for expansion. Portable containers and gas tanks should be filled 3/4 full.
Never move, load or transport a chipper/shredder while the engine is running. First, shut off the power supply, wait for all moving parts to come to a complete stop and then disconnect the spark plug wire (if applicable).
When towing, be sure to connect safety hitch chains and tighten and secure trailer hitch bolts. Rotate the chipper/shredder's discharge chute in a direction where it will not strike objects along the roadway. Equipment should only be towed at the manufacturer's recommended speed.
If the chipper/shredder is operated near a roadway, make sure it is positioned far enough away to not interfere with the flow of traffic or injure passers by. Use flags and warning signs to alert motorists that there are employees in the area. These employees should wear highly reflective vests. Ensure the discharge chute is pointed away from the roadway as well. This will keep debris from flying toward traffic.
Accident Report
Chipper Overturns on Employee |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 111895140
An employee was sitting on a chipper that was loaded on a trailer. As the trailer was moving, it hit a hole in the ground and the chipper tipped over. The employee's hand was pinned between the chipper and the ground. He sustained severe cuts to his left hand.
 Never sit on any part of the equipment under any circumstance. Never sit on any part of the equipment under any circumstance.
|
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
For answers, click here.
- The manufacturer's recommended speed
- Level
- Five
- Latched
- Allergies
- Signs
- To set up a chipper/shredder for operation, choose a surface that is ____________.
- Before operating the chipper/shredder, check to see that the hood is closed and _______________.
- When working outside, it is important to know if your coworkers have any severe ____________.
- The gas tank should be filled after the engine has cooled for at least _________ minute(s).
- When towing a chipper/shredder, your speed should never exceed _____________________________.
- When working near traffic, use flags and warning _______ to alert motorists that there are employees in the area
- Develop safe feeding procedures.
- Recognize how to protect yourself from moving parts.
Materials should be fed into the chipper/shredder safely, to avoid contact with the equipment's moving parts. Follow these feeding procedures to keep you safe.
- Feed material only when the chipper/shredder is at full operating speed.
- Feed branches from the side of the chute, not in front of it. This will reduce the risk of you being caught and dragged into the machine. Standing to the side of the equipment will also make it easier for you to reach the emergency shut-off switch in the event of an accident.
- Keep hands and feet outside of the feed chute.
- Use a push stick to help feed small pieces and brush through the chipper/shredder to keep you at a distance from the machine's moving parts. Do not push materials into the chute with your hands or feet, pitch forks, shovels, etc.
- Let go of material as soon as it begins to be pulled into the machine and walk away to avoid being hit or dragged into the chipper by limbs you are feeding.
- Feed the branches butt end first to keep the chipper from being jammed and to reduce the kickback of material.
- Lay shorter pieces of material on top of longer pieces and feed through the machine.
- Collect small materials such as leaves and twigs and put them with the chipped material instead of feeding them through the chipper/shredder.
YES
Use a push stick to feed small pieces of brush.
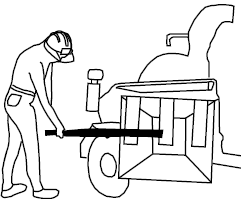
|
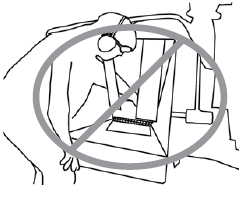
NO
Never push brush into the chipper/ shredder with your arm or leg.
|
Follow these steps to avoid losing body parts or your life in the equipment's moving parts.
- Never leave the chipper/shredder unattended. This helps protect children and unauthorized persons who may go near the equipment.
- Never inspect or work on equipment while it is running. This will protect you from the machine's moving parts.
- Never operate the chipper/shredder without all guards in place. These guards were put on the machine by the manufacturer to keep you from being caught in moving parts. Never remove or redesign these guards.
- Keep hands and feet away from all moving parts.
- Before attempting to unclog debris or make adjustments:
- Shut off engine.
- Disconnect spark plug wire or battery cables (if equipped).
- Remove key.
- Disconnect PTO shaft (if equipped).
- Wait for all parts to stop moving.
- Eliminate tripping hazards by clearing all brush and debris from the front and sides of the machine. This will keep you from falling into its moving parts.
- Never climb or sit on the chipper/shredder while it is running.
Accident Report
Operator's Foot Amputated in Chipper |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 100746346
The operator of a chipper was feeding small branches with his foot. The foot became caught in the infeed rollers and was pulled into the chipper. His right foot and ankle were amputated.
 Never feed material any part of your body. Always use a push stick. Never feed material any part of your body. Always use a push stick.
|
Accident Report
Employee Loses Hand in Chipper |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 125903088
An employee was operating a chipper that became jammed. He climbed on top of the chipper and unfastened the hood. His hand slipped into the rotating blades and was cut off at the wrist.
 Shut off the machine and wait for all parts to stop moving before servicing equipment. Shut off the machine and wait for all parts to stop moving before servicing equipment.
|
A rotating PTO shaft can quickly catch your clothing or hair and wrap your body around the shaft, killing you before you can react. However, PTO accidents are preventable. Follow these steps to safely work around PTO shafts.
- Never operate equipment without the PTO shields in place.
- Ensure the shaft is secured to the tractor.
- Keep all bystanders, especially children away from the shaft.
- Keep hands, feet, clothing and hair away from the shaft.
- Walk around a PTO shaft, never step over it.
- Never inspect, service, lubricate or adjust the PTO unless the PTO is disengaged, the tractor engine is shut off and the shaft has stopped rotating.

Never Operate Equipment
Without a PTO Guard. |
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
For answers, click here.
- PTO shaft
- Let go
- Side
- Butt end
- Inspect
- Reach
- All guards
- When feeding material, feed from the ________ of the chute.
- Branches should be fed into the chipper/shredder _________ first.
- Never operate a chipper/shredder without _________ in place.
- A rotating __________ can quickly catch your clothing or hair and wrap your body around it.
- Never _________ into the infeed hopper.
- Do not __________ or work on equipment while the engine is running.
- ___________ of material as soon as it begins to be pulled into the chipper/shredder.
- Recognize how to prevent injury from the chipper/ shredder hood.
- Identify the location of the hood on different chipper/shredder models.
- View different warning labels on chipper/shredder hoods.
NOTE: The following information has been covered in previous chapters. Due to the seriousness of this issue, please review the information.
The hood that covers the chipper/shredder's rotating blades can fly off and seriously injure or kill you. Take the following steps to protect you from the equipment's hood.
- Check to see that the hood latch is secured. Check for any missing parts or hinges that may allow the hood to become loose.
- When starting the machine, unless the manufacturer recommends otherwise, begin by running it at the lowest possible speed and then increase to full operating speed while listening for unusual vibrations indicating loose or broken parts. Stop the engine immediately if there is any unusual noise.
- Do not attempt to open or close the hood of the chipper while it is running. Close the hood before starting the engine.
- After turning off the engine, wait for all parts to stop moving and disconnect the spark plug wire or drive shaft before opening the hood.
Accident Report
Operator Struck by Chipper Hood |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 106387681
The operator of a running chipper went near the hood and removed the top pin. The hood flew off and struck him in the face and chest, killing him.
 Shut off the machine and wait for all moving parts to stop before opening the hood. Shut off the machine and wait for all moving parts to stop before opening the hood.
|
Accident Report
Hood Strikes Operator's Chest |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 102782224
The operator of a chipper removed the hood covering the blade without shutting the machine off. The rotating blade struck the hood, ripped it off its hinges and threw it at the operator, striking him in the chest. The operator died.
 Never open or remove the hood of a running chipper/shredder. Never open or remove the hood of a running chipper/shredder.
|
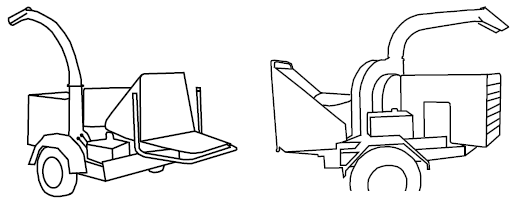
As different models of wood chippers vary, so does the location of the hood. Below are illustrations of different types of chippers with a reference arrow or bracket pointed at the hood.
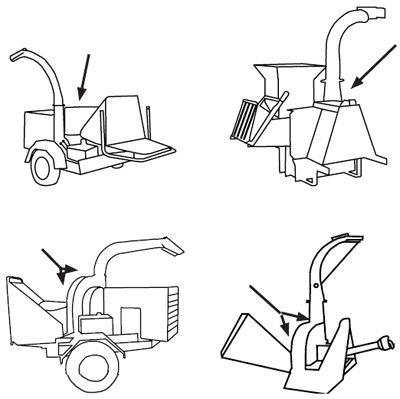
Below are examples of warning labels you might see on or around chipper/shredder hoods.
|
Knife can cut
off your hand. |
| DANGER
DO NOT OPEN WHEN
CHIPPER IS RUNNING |
DANGER |
DO NOT OPEN
OR CLOSE HOOD WHEN CHIPPER
IS RUNNING |
Warning label on hood
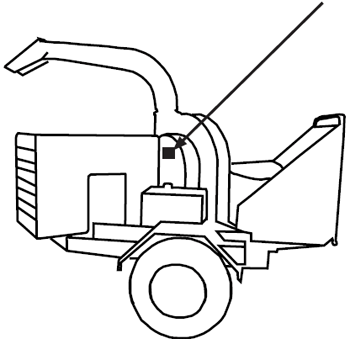 |
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
For answers, click here.
- Stop
- Open
- Close
- Parts
- Never operate a chipper/shredder with the hood __________.
- After turning off the engine, wait for all moving parts to come to a complete ____________ before inspecting the machine or opening the hood.
- _______ the chipper/shredder hood before starting the engine.
- Check for any missing ________ or hinges prior to operation.
- Locate the hood on the following models.
- Identify environmental hazards.
- Recognize treatment and first aid for exposure to environmental hazards.
You can become seriously ill or die if you do not take the proper precautions while working in high temperatures and humidity. Heat can reduce physical performance, as well as mental alertness, causing more accidents.
Heat Facts
- You are more likely to suffer from a heat related illness on humid days.
- If you are not used to working in the heat, you are more likely to suffer from a heat related illness. It can take your body anywhere from 5 days to 2 weeks to be acclimated to working in the heat. It is recommended that new workers who begin in hot, humid weather, start out by working half of the normal time and workload on the first day and then build up to a complete day by the end of the week.
- You are more vulnerable to heat illness if you have suffered in the past.
- During the course of the day, you can produce as much as 2 to 3 gallons of sweat. Replenish this fluid by drinking liquids so that you do not suffer from a heat related illness.
Accident Report
Employee Dies of Heat Stroke |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 014444699
An employee was dragging tree branches and feeding them into the chipper. Shortly before noon, the temperature had risen into the 80s. The employee became overheated and collapsed. He was taken to the hospital where he was pronounced dead due to heat stroke.
 Take frequent, short breaks and drink plenty of water to keep yourself cool and hydrated. Take frequent, short breaks and drink plenty of water to keep yourself cool and hydrated.
|
- If someone feels overheated, move them into a cooler, preferably air conditioned area. Watch the person and seek medical attention if needed.
- Fan the person in order to increase cooling.
- Have the person drink plenty of fluids.
- If the person goes into convulsions or shows symptoms of heat stroke, call 911 immediately and take steps to cool them down such as soaking their clothing in cool water.
Heat Exhaustion Symptoms
Heat exhaustion is a serious illness and needs to be treated immediately before a heat stroke occurs. If you or a coworker experience any of the following symptoms, cool off immediately and drink plenty of water.
- Dizziness
- Light headedness
- Headache
- Feeling weak, fatigued
- Clammy and moist skin
|
Heat Stroke Symptoms
Heat Stroke is a medical emergency that can become fatal. If anyone experiences the following symptoms of heat stroke, call 911 immediately.
- Hot, dry, red skin (not sweaty)
- Disorientation
- Confusion
- Body temperature greater than 105º F
- Convulsing
- Unconsciousness
|
It is important to keep yourself hydrated and cool while working outside.
- Drink water often throughout the day; don't wait until you're thirsty to get a drink. At least a quart of water per hour is recommended.
- Stay away from soda, coffee, tea and alcoholic drinks that dehydrate the body.
- Avoid large meals before working in the heat.
- Some prescriptions can make you more susceptible to heat illnesses. Check with your doctor or pharmacist to see if any medicine you are taking could affect you while working in the heat.
- Wear light-weight fabric, such as cotton, to help keep your body cool.
- Wear a hat or sun visor on sunny days to help control body temperature.
- Plan to do the heaviest work at the coolest part of the day. This is usually between 6 a.m. and 10 a.m.
- Take frequent, short breaks in shaded areas to cool down.
- Do not take salt tablets, unless recommended by your doctor. Most people receive enough salt in their diet to account for the salt that is lost through sweating.
Prolonged exposure to sunlight causes skin cancer, cataracts and other serious illnesses.
- Choose a sunscreen that is marked broad-spectrum. This will protect you from both UVA and UVB rays. Ensure the Sun Protection Factor (SPF) is at least 15.
- Wear a hat or sun visor, sunglasses, and lightweight long-sleeve shirts and pants on sunny days to help control body temperature and block the sun.
Lightning strikes injure and kill hundreds of people each year. Follow these precautions to help keep you safe when the weather turns bad.
- As soon as you hear thunder, shut off and put away equipment and move indoors out of the storm. When you are able to hear thunder, you are able to be struck by lightning. Lightning can strike even when it's not raining.
- The cab of an enclosed vehicle provides some protection from lightning but a sturdy building provides the best protection.
- Listen to the radio for weather updates and storm warnings.
- Get to a low space. Lightning strikes the tallest objects.
- Crouch down on the balls of your feet. Place your hands on your knees and lower your head between your knees.
- Minimize contact with the ground.
- Do not lie flat on the ground. This will make you a larger target.
- Large, lone trees and towers, fences, telephone poles and power lines.
- Rivers, lakes, pools and other bodies of water.
- Metal objects, tools, equipment, wire fences and umbrellas.
- Call 911
- Check to see if they're breathing. Rescue breathing or CPR may be required.
- Check for burns on their body.
- Move the victim inside, out of the storm.
- Note: Most lightning-strike victims survive with immediate treatment and rescue breathing or CPR.
| Lightning Facts |
 |
A person that is struck by lightning DOES NOT retain an electric charge that can shock you. |
 |
Lightning can spread as far as 60 feet after striking the ground. |
 |
Lightning can travel at speeds of 100,000 mph. |
 |
The temperature of a bolt of lightning can be as high as 50,000º F. |
 |
Lightning CAN strike the same place twice. |
Prolonged exposure to freezing temperatures can result in cold induced injuries and illnesses that can seriously injure or kill you.
Cold temperatures reduce mental alertness and cause fatigue and exhaustion that can lead to accidents.
Frostbite
Frostbite occurs when parts of the body become so cold that the skin and tissue freezes. Frostbite normally occurs on ears, nose, fingers, hands, toes and feet or other parts of the body that are left uncovered in below-freezing temperatures. Frostbitten skin becomes numb and turns a pale white color.
Hypothermia
Hypothermia occurs when a person's body temperature drops to or below 95º F. Common symptoms include bluish-colored skin, uncontrollable shivering and drowsiness or fatigue.
Avoid Cold-Induced Injuries and Illnesses
- Layer clothing when working in cold temperatures; you can easily take off layers if you are too warm.
- Wear a hat and gloves.
- Keep muscles warm and loose by moving as much as possible.
- Take frequent, short breaks in warm areas.
- Perform work at the warmest part of the day, typically in the afternoon.
- Never work alone.
What to Do If Someone's Suffering from a Cold-Induced Injury or Illness
- Move the person out of the cold and into an area that is warm and dry.
- Remove wet and tight clothing and cover the person with a blanket.
- Never rub the affected area. This will cause further skin and tissue damage.
- Seek medical attention immediately.
Insect stings can be treated without medical attention unless the person suffers an allergic reaction.
The first step to treating an insect sting is to remove the stinger. This can be done by using a straight edge to scrape off the stinger or by using tweezers to pull it out. If you choose to use tweezers to remove the stinger, use extreme caution to not puncture the protruding venom sac.
After the stinger has been removed, a cold pack can be used during the first 24 hours to suppress pain and swelling. Following the first 24 hours, heat should be applied if pain or swelling persist.
Those with severe allergies to insect stings should consult a physician about carrying a prescription medical kit. The kit contains medicine and instructions to be used if the person is stung. If the kit is used, the victim still must receive medical attention. Call for help or take them to the nearest hospital.
If you are bitten by a snake, seek medical attention immediately and try to describe the size and color of the snake to the doctor. This can help the doctor determine whether or not the snake was poisonous. Never cut, suck or apply cold packs to snake bites.
Be aware of animals such as squirrels or bats that may be in trees or bushes and startle you during work. Also, be cautious of animals such as rats, skunks and raccoons that could be rabid.
- Wash the affected area and all clothing and tools that may have touched the plant.
- Avoid scratching the area if possible, to prevent infection.
- Hot and cold compresses can be used to suppress itching.
- Consult a doctor if the rash is on the face, inside the mouth or covers a large portion of the body.
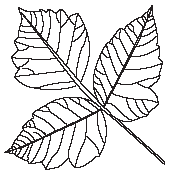 |
Poison Ivy Leaves are usually found in clusters of three. |
Minor cuts and burns can be treated on the job site.
Seek medical attention if:
- Cuts are severely bleeding, more than one-half inch long and one-quarter inch deep, or the result of a puncture wound.
- Burn area covers more than one-fifth of the body with blisters, blisters occur on the hands, feet, face or genitalia, or if the skin is blackened or charred.
Treating Cuts
- Clean the area thoroughly.
- Remove any debris that may be in the wound.
- Apply pressure to the wound using gauze or a clean, absorbent cloth until the bleeding stops. If blood seeps through the cloth, do not remove it, continue adding more gauze or cloth over the previous one.
- Apply an antibiotic ointment and cover with a bandage or clean gauze.
- Allow wound to heal and keep dirt from creating infection by changing the bandage or gauze frequently.
- If a limb has been amputated, elevate while applying direct pressure and call 911.
Treating Burns
- Cool the burn by placing it under cool running water or in a container of cool water for at least 15 minutes.
- Cover the area with gauze or a clean cloth.
- Allow burn to heal and keep dirt from creating infection by changing the gauze frequently.
- If blisters occur, do not break them. Cover with gauze and allow them to break on their own.
The following is a list of minimum requirements for workplace first aid kits as outlined by ANSI Standard Z308.1-2003*.
- absorbent compress
- adhesive bandages
- adhesive tape
- individual-use antiseptic applications
- individual-use burn treatment applications
- latex-free medical exam gloves
sterile pads
- triangular bandage
*ANSI Z308.1-2003 is published by the International Safety Equipment Association, Arlington, VA www.safetyequipment.org. Used with permission.
Choose the correct answer. For answers, click here.
- Stop a cut from bleeding by applying ______________.
- Aloe
- Ointment
- Direct pressure
- Dizziness, light headedness, headache and fatigue are all symptoms of _____________.
- Lightning strike
- Heat exhaustion
- It is important to take frequent, short _________ when working outside.
- Strides
- Phone calls
- Breaks
- To keep myself hydrated when working outside, I should drink __________.
- Water frequently throughout the day
- Only when I'm thirsty
- Soda at lunchtime
- Lightning strikes the ________ objects.
- Tallest
- Widest
- Shortest
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
- Immediately
- Stinger
- Wash
- Frostbitten
- Lower
- Never rub and area that has been _____________.
- The first step to treating an insect sting is to remove the _____.
- If you contact poison ivy, oak or sumac, ______ the affected area as well as all clothing and tools.
- Hypothermia occurs when body temperature drops to 95° or ___________.
- If a person with a known allergy to insects is stung, call for help ___________________.
Wood chippers/shredders can seriously injure or kill if not operated
correctly. On the job accidents can be avoided by developing safe
work habits before, during and after machinery operation.
You have been presented with checklists, safety tips and exercise
designed to help you avoid the most commonly reported causes
of wood chipper/shredder operation injuries and deaths, as well as
other important safety precautions to consider. Use this information
to keep your work experience safe.
Choose the correct answer.
For answers, click here.
- What are the two most commonly reported causes of serious
injury and death from operating wood chippers/shredders?
- Cuts and burns
- Dehydration and fatigue
- Being caught in moving parts & being struck by the hood
- A pre-start inspection should be performed __________.
- Whenever is convenient
- Once a month
- At the start of each work shift
- A chipper should never be operated with the hood ________.
- Open
- Closed
- A chipper/shredder should be operated on a _______ surface.
- Concrete
- Gravel
- Level
- When feeding brush into the chipper, use a ________ to push small pieces through.
- Leg
- Push stick
- Pitch fork
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
a. Coolest
b. Guard
c. Thunder
d. Large meals
e. Call 911
- PTO-powered equipment should never be operated without a __________.
- If a limb has been amputated, elevate it, apply direct pressure, and _________________.
- The heaviest work should be done at the _____________ part of the day.
- Avoid __________ before working in the heat.
- If you can hear ________ then you are able to be struck by lightning.
Choose the correct answer.
- What are the two most commonly reported causes of serious injury and death from operating wood chippers?
- Being caught in moving parts & being struck by the hood
- Being struck by lightning & heat stroke
- Being struck by debris & burns
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
a. Danger
b. Hard hat
c. Alcohol
d. Triangle
- Do not operate machinery if you are under the influence of drugs or c. Alcohol .
- The d. Triangle shape is the symbol for caution.
- A b. Hard hat should be worn at all times when operating a chipper/shredder.
- a. Danger is the most serious safety message.
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
- The manufacturer's recommended speed
- Level
- Five
- Latched
- Allergies
- Signs
- To set up a chipper/shredder for operation, choose a surface that is b. Level.
- Before operating the chipper/shredder, check to see that the hood is closed and d. Latched.
- When working outside, it is important to know if your coworkers have any severe e. Allergies.
- The gas tank should be filled after the engine has cooled for at least c. Five minute(s).
- When towing a chipper/shredder, your speed should never exceed a. The manufacturer's recommended speed.
- When working near traffic, use flags and warning f. Signs to alert motorists that there are employees in the area
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
- PTO shaft
- Let go
- Side
- Butt end
- Inspect
- Reach
- All guards
- When feeding material, feed from the c. Side of the chute.
- Branches should be fed into the chipper/shredder d. Butt end first.
- Never operate a chipper/shredder without g. All guards in place.
- A rotating a. PTO shaft can quickly catch your clothing or hair and wrap your body around it.
- Never f. Reach into the infeed hopper.
- Do not e. Inspect or work on equipment while the engine is running.
- b. Let go of material as soon as it begins to be pulled into the chipper/shredder.
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
- Stop
- Open
- Close
- Parts
- Never operate a chipper/shredder with the hood b. Open.
- After turning off the engine, wait for all moving parts to come to a complete a. Stop before inspecting the machine or opening the hood.
- c. Close the chipper/shredder hood before starting the engine.
- Check for any missing d. Parts or hinges prior to operation.
- Locate the hood on the following models.
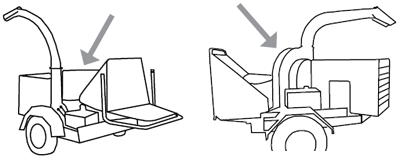
Choose the correct answer.
- Stop a cut from bleeding by applying ______________.
- Aloe
- Ointment
- Direct pressure
- Dizziness, light headedness, headache and fatigue are all symptoms of _____________.
- Lightning strike
- Heat exhaustion
- It is important to take frequent, short _________ when working outside.
- Strides
- Phone calls
- Breaks
- To keep myself hydrated when working outside, I should drink __________.
- Water frequently throughout the day
- Only when I'm thirsty
- Soda at lunchtime
- Lightning strikes the ________ objects.
- Tallest
- Widest
- Shortest
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
- Immediately
- Stinger
- Wash
- Frostbitten
- Lower
- Never rub and area that has been d. Frostbitten.
- The first step to treating an insect sting is to remove the b. Stinger.
- If you contact poison ivy, oak or sumac, c. Wash the affected area as well as all clothing and tools.
- Hypothermia occurs when body temperature drops to 95º or e. Lower.
- If a person with a known allergy to insects is stung, call for help a. immediately.
Choose the correct answer.
- What are the two most commonly reported causes of serious injury and death from operating wood chippers/shredders?
- Cuts and burns
- Dehydration and fatigue
- Being caught in moving parts & being struck by the hood
- A pre-start inspection should be performed __________.
- Whenever is convenient
- Once a month
- At the start of each work shift
- A chipper should never be operated with the hood ________.
- Open
- Closed
- A chipper/shredder should be operated on a _______ surface.
- Concrete
- Gravel
- Level
- When feeding brush into the chipper, use a ________ to push small pieces through.
- Leg
- Push stick
- Pitch fork
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
a. Coolest
b. Guard
c. Thunder
d. Large meals
e. Call 911
- PTO-powered equipment should never be operated without a b. Guard.
- If a limb has been amputated, elevate it, apply direct pressure, and e. Call for 911.
- The heaviest work should be done at the a. Coolest part of the day.
- Avoid d. Large meals before working in the heat.
- If you can hear c. Thunder then you are able to be struck by lightning.
Publication #: MF2710
This material was produced under grant number 46G3-HT04 from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U.S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. government.
This booklet was produced by K-State Research and Extension, Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas.
The information in this publication has been compiled from a variety of sources believed to be reliable and to represent the best current opinion on the subject. However, neither K-State Research and Extension nor its authors guarantee accuracy or completeness of any information contained in this publication, and neither K-State Research and Extension or its authors shall be responsible for any errors, omissions, or damages arising out of the use of this information. Additional safety measures may be required under particular circumstances.
Brand names appearing in this publication are for product identification purposes only. No endorsement is intended, nor is criticism implied of similar products not mentioned.
Disclaimer
and Reproduction Information: Information in NASD does not
represent NIOSH policy. Information included in NASD appears
by permission of the author and/or copyright holder. More
Disclaimer and Reproduction Information: Information in
NASD does not represent NIOSH policy. Information included in
NASD appears by permission of the author and/or copyright holder.
More

![]() The triangle shape is the symbol for caution. The exclamation mark in the center means Pay Attention. In some instances, the triangle-shaped sign will show a picture. Other times, words explain why the sign is used.
The triangle shape is the symbol for caution. The exclamation mark in the center means Pay Attention. In some instances, the triangle-shaped sign will show a picture. Other times, words explain why the sign is used.