Contents
Introduction What’s Inside?
Lesson 1 Take Control of Your Own Safety
Lesson 2 Avoid Shock & Electrocution
Lesson 3 Preventing Falls from Trees
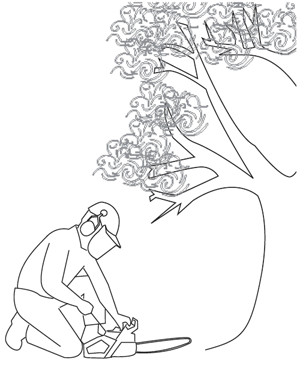
Lesson 4 Avoid Being Struck by Trees or Limbs
Lesson 5 Environmental Hazards
Conclusion
Quiz Yourself Solutions
This booklet teaches important safety practices to be followed when manually trimming trees.
Safety tips, along with real accident reports, have been combined to help you protect yourself from the hazards involved in this type of work.
Use this booklet in conjunction with hands-on safety training and equipment operator’s manuals.
Lesson 1 Take Control of Your Own Safety
Objectives
Greatest Dangers
The most common types of serious tree trimming accidents are:
| Accident Report Employee Electrocuted When Branch Falls on Line |
Summary OSHA Accident Inspection 1099688358 An employee was trimming a tree that was near an overhead power line. The employee misjudged the distance, cut the branch, and it fell on the line. The employee, who was still holding onto the branch, was electrocuted.
|
| Accident Report Employee Falls After Disconnecting Both Lanyards |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 126621820 While working in a tree, an employee disconnected one lanyard to move around some limbs. After climbing approximately 60 feet up the tree, he disconnected the second lanyard before reconnecting the first. The employee fell and died of head injuries.
|
| Accident Report Employee Struck by Falling Limb |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 125616698 An employee was felling trees in a forested area when a limb fell from an adjacent tree and struck him on the head. The employee was killed.
|
Help Yourself
Safe work habits are important. Here are three important actions you can take to be safe on the job site.
Safety Messages and Signs
Manufacturers put important safety messages on each piece of equipment and in the operator’s manual. It is critical to read, understand and follow all safety messages.
![]() The triangle shape is the symbol for caution. The exclamation mark in the center means Pay Attention. In some instances, the triangle-shaped sign will show a picture. Other times, words explain why the sign is used.
The triangle shape is the symbol for caution. The exclamation mark in the center means Pay Attention. In some instances, the triangle-shaped sign will show a picture. Other times, words explain why the sign is used.
Many safety messages use the words Caution, Warning and Danger to get your attention. Following are safety messages and their meanings. Each of these signs will have a written message, and perhaps a picture, about a possibly unsafe condition.
CAUTION means you need to be careful. Follow the directions on the sign or you could get hurt.

WARNING is more serious and means you need to follow the directions on the sign or you could be badly hurt or killed.

DANGER is the most serious safety message. If you don’t follow the directions, you will be seriously injured or killed.

Images displayed in the caution, warning and danger boxes have been recreated from images taken with permission from ASAE S441.4, FEB04, Safety Signs.
Protective Equipment
Certain equipment is necessary to protect you while trimming trees. The following protective equipment is required.
Hard Hat
A hard hat should be worn to protect your head from falling limbs.
Gloves
Gloves may be worn to protect your hands from puncture wounds and cuts.
Sturdy, Non-Slip Boots
Wear boots to keep a firm footing on the ground and reduce the risk of slipping and falling.
Climbing Equipment
Safety harnesses, belts, ropes, lanyards, slings and carabiners appropriate to the job are used to keep you secured in the tree.
When Operating a Chainsaw You Must Wear:
Leg Protection
Leg protection must be worn when performing ground operations. The material should be cut-resistant and cover the entire thigh to the top of each boot.
Goggles or Safety Glasses
Goggles or safety glasses must be worn at all times to protect your eyes from foreign objects.
Face Shield
A face shield should be worn to protect your face from the kickback of the machine and debris.
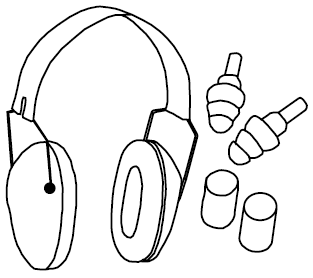
Hearing protection.
Over time, you will lose your hearing if you are exposed to loud noises without protection.
Two common types of hearing protection are muffs and plugs. Ear muffs should seal around your ears to properly muffle loud noises. Wash reusable ear plugs with warm, soapy water after each use in order to prevent infection. Discard disposable ear plugs after each use.
When to Wear Hearing Protection
OSHA Standard 1910.95 (i) (l) requires hearing protection to be worn when sound levels exceed certain limits (generally, a daily average of 85 or 90 decibels, depending on the circumstances). These levels can be measured with a dosimeter. A hearing conservation program requiring hearing tests and other precautions may also be necessary. Check with the equipment operator’s manual, as well as your supervisor, for suggestions on hearing protection for each piece of equipment and instructions on how to wear it properly.
Hearing Protection Rules of Thumb
Hearing protection may be needed if:
| Pre-Start Checklist | |
| Tree | |
| Trunk free of cracks, splits or cankers. | |
| No nests, hives or other signs of animal life. | |
| No signs of poison ivy or oak. | |
| Equipment | |
| Belts and harnesses free of cracks, cuts and broken stitching. | |
| Clips, buckles and rivets not loose or broken. | |
| Ropes and lanyards are dry and show no signs of fraying, intense wear or sun damage. | |
| Snap catches and carabiners close securely and are the appropriate size for the D-rings in use. | |
| Location | |
| Warning signs and rumble strips are being used, when necessary, if the site is near a roadway. | |
| Cones and flaggers are used to divert traffic, when necessary. | |
| Following the inspection, should you find any hazards while climbing, descend the tree immediately and take appropriate action to solve the problem. | |
Pre-Start Inspection
A hazard briefing must be performed before the start of each job. During this briefing, you and your supervisor should analyze the potential dangers of performing the job. Based on the analysis, choose a plan of attack and proper equipment that will help you carry out the job safely.
Tree
Ensure the trunk is stable by looking for cracks, splits and cankers. Look for any dead and rotten branches. Watch for any nests, hives, or other signs that animals may be in the tree. Look for poison ivy or oak growing on or around the tree.
| Accident Report Employee Suffers Infection |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 119705770 An employee was trimming trees when his arm came in contact with poison oak. He suffered an allergic reaction and infection set in his arm before transferring to his leg. He was hospitalized for treatment.
|
Equipment
Check belts and harnesses for any cracks, cuts or broken stitching. Ensure that all clips, buckles and rivets are not loose or broken. Check ropes and lanyards for signs of fraying and intense wear. Do not use a rope that is wet, has been driven over or has been stored in the sun. These factors will weaken the elasticity and strength of the rope. Check snap catches and carabiners to make sure they will close securely and are the appropriate size for the D-ring on your harness or belt.
Location
If working near roadways, use warning signs and rumble strips, when necessary, to alert motorists that employees are in the area. Use cones and flaggers (wearing highly-reflective vests) to divert traffic away from the area where work is being performed.
Quiz Yourself
Answers can be found here.
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
Lesson 2 Avoid Shock and Electrocution
Objectives
Qualified vs. Unqualified
Only qualified line-clearance tree trimmers are allowed within 10 feet of energized power lines. According to OSHA, qualified employees are “those who are knowledgeable in the construction and operation of electric power generation, transmission, or distribution equipment involved, along with the associated hazards.” To become a qualified line-clearance tree trimmer, you will need additional training that is beyond the scope of this book.
Qualified and unqualified employees are required to keep the minimum distances found in the tables in the next section.
Electrical Hazards
You must use extreme caution when working around electrical lines. Electrocution can occur by direct contact, indirect contact or electrical arcing.
| Accident Report Employee Leans Backward Into Power Line |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 119596658 While descending a tree, an employee leaned back into a power line. He remained in contact with the 7.2-kilovolt power line for about 30 seconds before being thrown free. His supervisor performed CPR until emergency medical services arrived. The employee died of electrocution.
|
| Accident Report Employee Shocked When Saw Touches Line |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 123168965 An employee was trimming trees from the bucket of an aerial lift. The employee received an electric shock when his saw contacted a 13.2-kilovolt overhead power line.
|
| Accident Report Employee Electrocuted |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 123561540 A tree trimmer was cutting a branch when a gust of wind blew the branch into contact with a 35-kilovolt power line. The trimmer, who was touching the branch and tree was electrocuted.
|
| Accident Report Employee Electrocuted by Electrified Ground |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 301183893 A crew was cutting down a tree when it fell into a power line, breaking it. The line arced and bounced around. An employee ran in front of the truck and was electrocuted because the ground was electrified. His coworkers dragged him from the area, called for help, and performed CPR. The employee died 45 minutes after the accident.
|
Minimum Approach Distances
Always assume that electrical lines are energized and work beyond the following minimum distances to avoid contact. When you must work closer than the minimum distances, contact the power company to have the lines de-energized or shielded.
Minimum approach distances not only apply to employees, but also to all equipment, including ladders and aerial devices.
Minimum Approach Distances for Unqualified Employees
| Nominal Voltage kV Phase to Phase* | Distance |
|
| ft-in | m | |
| 0.0 to 1.0 | 10-00 | 3.05 |
| 1.1 to 15.0 | 10-00 | 3.05 |
| 15.1 to 36.0 | 10-00 | 3.05 |
| 36.1 to 50.0 | 10-00 | 3.05 |
| 50.1 to 72.5 | 10-09 | 3.28 |
| 72.6 to 121.0 | 12-04 | 3.76 |
| 138.0 to 145.0 | 13-02 | 4.00 |
| 161.0 to 169.0 | 14-00 | 4.24 |
| 230.0 to 242.0 | 16-05 | 4.97 |
| 345.0 to 362.0 | 20-05 | 6.17 |
| 500.0 to 550.0 | 26-08 | 8.05 |
| 785.0 to 800.0 | 35-00 | 10.55 |
| *Exceeds phase to ground. | ||
Chart taken from ANSI Z133.1-2000. Used with permission.
Minimum Approach Distances for Qualified Employees
| Nominal Voltage kV Phase to Phase* | Includes 1910.269 elevation factor,sea level to 5,000 feet* |
Includes 1910.269 elevation factor, 5,001 -10,000 feet* |
Includes 1910.269 elevation factor, 10,001 - 14,000 feet* |
|||
ft-in |
m |
ft-in |
m |
ft-in |
m |
|
| 0.5 to 1.0 | Avoid Contact |
Avoid Contact |
Avoid Contact |
|||
| 1.1 to 15.0 | 2-04 | 0.71 | 2-08 | 0.81 | 2-10 | 0.86 |
| 15.1 to 36.0 | 2-09 | 0.84 | 3-02 | 0.97 | 3-05 | 1.04 |
| 36.1 to 46.0 | 3-00 | 0.92 | 3-05 | 1.04 | 3-09 | 1.14 |
| 46.1 to 72.5 | 3-09 | 1.14 | 4-03 | 1.30 | 4-07 | 1.40 |
| 72.6 to 121.0 | 4-06 | 1.37 | 5-02 | 1.58 | 5-07 | 1.70 |
| 138.0 to 145.0 | 5-02 | 1.58 | 5-11 | 1.80 | 6-05 | 1.96 |
| 161.0 to 169.0 | 6-00 | 1.83 | 6-10 | 2.08 | 7-05 | 2.26 |
| 230.0 to 242.0 | 7-11 | 2.41 | 9-00 | 2.75 | 9-09 | 2.97 |
| 345.0 to 362.0 | 13-02 | 4.02 | 15-00 | 4.58 | 16-03 | 4.96 |
| 500.0 to 550.0 | 19-00 | 5.80 | 21-09 | 6.63 | 23-06 | 7.17 |
| 765.0 to 800.0 | 27-04 | 8.34 | 31-03 | 9.53 | 33-10 | 10.32 |
| *Exceeds phase to ground; elevation factor per 29 CFR 1910.269. | ||||||
Chart taken from ANSI Z133.1-2000. Used with permission.
For future reference, please take a moment and circle the chart you are required to follow.
Quiz Yourself
Answers can be found here.
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
Choose One: I am a __________ line-clearance tree trimmer.
Lesson 3 Preventing Falls from Trees
Objectives
Avoid Injury from Falling
YES Position yourself on limbs, close to the trunk, that can support your weight.  |
NO Never stand on a limb that is not strong enough to fully support you.  |
| Accident Report Employee Falls From Ladder |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 200450096 An employee who was trimming trees put a ladder in the bed of a pickup to use it as a height extender. There were no support attachments on the ladder and the base section did not have secure footing. The employee fell off the ladder, approximately 14 feet, broke his neck and died.
|
Knots
Below are some knots commonly used for climbing. For a more complete list of knots and explanations on how and when to use them refer to:
Arborists Certification Study Guide,
International Society of Aboriculture
www.isa-arbor.com
Tree Climber’s Guide,
International Society of Aboriculture.
www.isa-arbor.com
National Tree Climbing Guide,
United States Department of Agriculture’s National Tree Climbing Program.
www.fs.fed.us/treeclimbing/
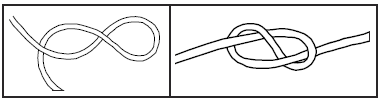
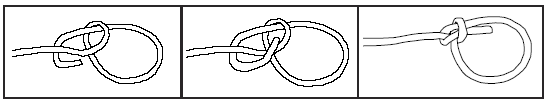
Figure Eight Knot
The figure eight knot can be used for a variety of purposes. Examples include but are not limited to:
Follow the steps below to tie a Figure 8 knot.
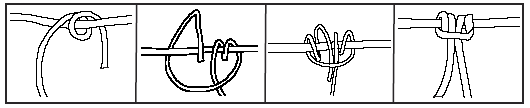
Prusik Knot
The Prusik is a friction knot. This means the knot can slide easily without tension. Examples include but are not limited to:
Follow the steps below to tie a Prusik knot.
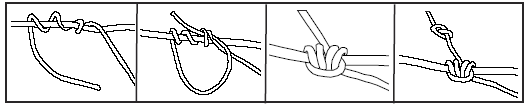
Blake’s Hitch
The Blake’s hitch is a modified version of the Prusik knot. It is also a friction knot. After making the hitch, the end should always be tied with a figure eight stopper knot.
Follow the steps below to tie a Blake’s hitch.
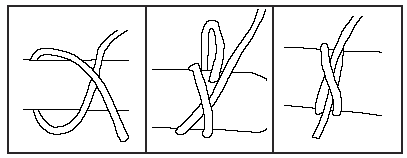
Clove Hitch
The Clove hitch is a knot that can be used to tie equipment to the end of the rope or to the tree. The Clove hitch should never be used as a lifeline.
Follow the steps below to tie a Clove hitch.
Bowline Knot
The Bowline knot is formed at the end of a rope and does not slip or tighten under stress. Examples include but are not limited to:
Follow the steps below to tie a Bowline knot.
Quiz Yourself
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below. Answers can be found here.
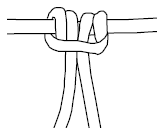 _________________ Knot
_________________ Knot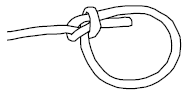 _________________ Knot
_________________ KnotLesson 4 Avoid Being Struck by Trees or Limbs
Objectives
Prevent Injury from Trees and Limbs
| Accident Report Falling Tree Strikes Employee on Head |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 111100657 An employee turned his back to a tree that was being trimmed. A limb struck the employee on the back of the head and killed him.
|
| Accident Report Limb Rebounds; Saw Strikes Employee |
OSHA Accident Inspection 125907865 An employee was using a chainsaw to cut a 3 inch diameter branch. After he had made the final cut, the branch fell and bounced after hitting a concrete walk. The cut limb struck the employee in the face and the chainsaw struck his right arm. He suffered deep cuts as well as nerve and tendon damage.
|
Using a Chainsaw
General Instructions:
| Accident Report Employee Cut by Chainsaw |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 120134390 An employee was standing on a slope cutting a log into pieces. He slipped on the damp ground and hit his upper left arm with the chainsaw. The arm was severely cut and the employee was hospitalized.
|
YES Start a chainsaw on the ground. 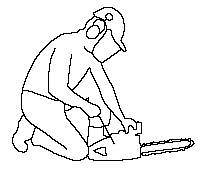 |
NO Never start a chainsaw against your body. 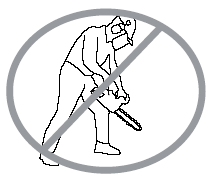 |
Kickback is a common cause of injury associated with chainsaws. Kickback occurs when the chain around the end of the bar contacts a hard object (such as a knothole) or when the teeth of the saw are pinched in the wood. This kicks the saw backward and upward, rapidly, where it can strike you.
To reduce kickback:
| Accident Report Employee Killed When Chainsaw Kicks Back |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 120169669 An employee was trimming trees and cutting downed limbs. The tip of his chainsaw struck a limb and kicked back, striking him across the neck. He died due to a severe cut to his throat.
|
YES Insert the blade fully to reduce kickback. 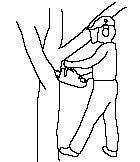 |
NO Do not cut with the tip of the blade. 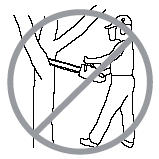 |
Trimming Branches
To safely trim branches, use three cuts to remove the branch completely.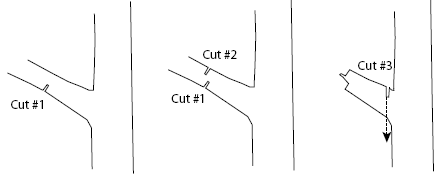
Felling Techniques
When a tree must be removed, there are several things to consider before cutting.
Inspect the Tree
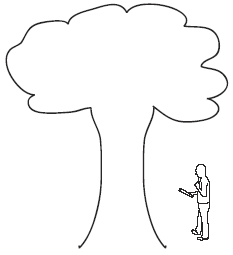
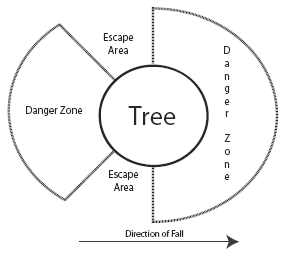
Locating the Escape Areas
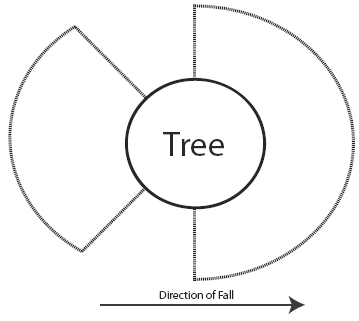
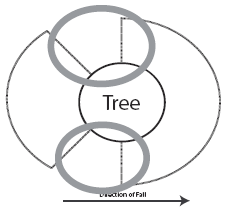
Before you begin to cut, you must determine your escape area. This is the area you will go to immediately after the back cut has been made and the tree is beginning to fall.
To locate the escape areas, you must first determine the danger zones. Two danger zones can be identified and must be avoided to prevent serious injury or death. The first danger zone is located in a semi-circle, from half the diameter of the tree toward the direction of the fall. The second danger zone is one-quarter of the diameter of the tree and located in the opposite direction of the intended fall. Fellers MUST avoid these two danger zones.
The escape areas are then located between the danger zones. Always retreat to one of these areas as the tree is beginning to fall.
| Accident Report Employee Struck by Falling Tree |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 114147440 An employee was working on the ground, cutting down a tree. When the tree fell, it struck him on the head, killing him.
|
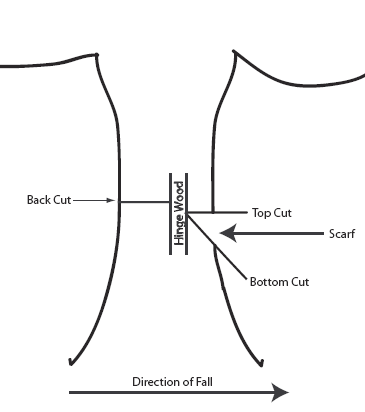
Making the Cut
There are three key parts to a successful felling.
Types of Notches
Note: The notches can be made at any height on the tree, but always start high enough to allow room to complete all three cuts.
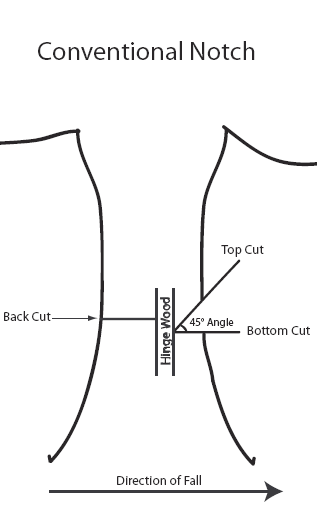
| Conventional Notch | |
| Top Cut: | Cut downward at a 45° angle to a point that is 1/4 to 1/3 the tree’s diameter. |
| Bottom Cut: | Cut straight across the tree until you reach the end point of the top cut. |
| Back Cut: | Start the cut 1 inch above the notched corner on the opposite side of the tree. Cut straight across, until you reach the hinge wood. |
| Common Cutting Mistakes | |
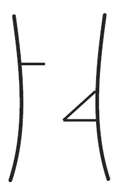 |
Back Cut is too high. Creates poor hinge. |
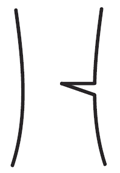 |
Bottom Cut is not steep enough to form a 45° angle. |
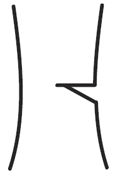 |
Endpoints do not meet. Dutchman's notch. |
For more information on logging operations visit www.osha.gov
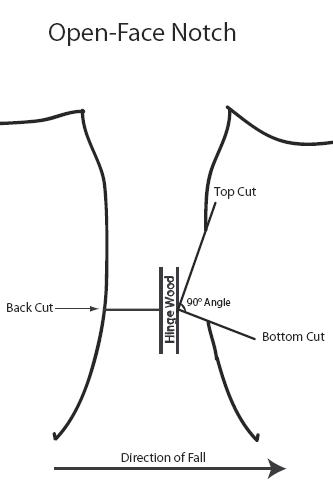
| Open-Face Notch | |
| Top Cut: | Cut downward at a 70° angle to a point that is 1/4 to 1/3 the tree’s diameter. |
| Bottom Cut: | Cut upward at a 20° angle until you reach the end point of the top cut. |
| Back Cut: | On the opposite side of the tree, cut straight across, at the same height of the notched corner, until you reach the hinge wood. |
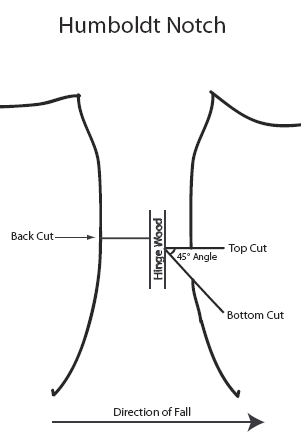
| Humboldt Notch | |
| Top Cut: | Cut straight across to a point that is 1/4 to 1/3 of the tree’s diameter. |
| Bottom Cut: | Cut upward at a 45° angle until you reach the end point of the top cut. |
| Back Cut: | Start out 1 inch above the notched corner on the opposite side of the tree. Cut straight across until you reach the hinge wood. |
Quiz Yourself
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below. Answers can be found here.
Lesson 5 Environmental Hazards
Objectives
Heat Stress
You can become seriously ill or die if you do not take the proper precautions while working in high temperatures and humidity. Heat can reduce physical performance, as well as mental alertness, causing more accidents.
Heat Facts
| Accident Report Employee Dies of Heat Stroke |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 014444699 An employee was dragging tree branches and feeding them into the chipper. Shortly before noon, the temperature had risen into the 80s. The employee became overheated and collapsed. He was taken to the hospital where he was pronounced dead due to heat stroke.
|
What to Do If Someone's Suffering from a Heat Illness
Heat Exhaustion Symptoms
|
Heat Stroke Symptoms
|
Avoid Heat Related Illnesses
It is important to keep yourself hydrated and cool while working outside.
Sun Exposure
Prolonged exposure to sunlight causes skin cancer, cataracts and other serious illnesses.
Lightning Precautions
Lightning strikes injure and kill hundreds of people each year. Follow these precautions to help keep you safe when the weather turns bad.
If You Can't Take Cover Inside
Keep Away From
If Someone is Struck by Lightning
| Lightning Facts | |
| A person that is struck by lightning DOES NOT retain an electric charge that can shock you. | |
| Lightning can spread as far as 60 feet after striking the ground. | |
| Lightning can travel at speeds of 100,000 mph. | |
| The temperature of a bolt of lightning can be as high as 50,000° F. | |
| Lightning CAN strike the same place twice. | |
Cold Induced Injuries and Illnesses
Prolonged exposure to freezing temperatures can result in cold induced injuries and illnesses that can seriously injure or kill you.
Cold temperatures reduce mental alertness and cause fatigue and exhaustion that can lead to accidents.
Frostbite
Frostbite occurs when parts of the body become so cold that the skin and tissue freezes. Frostbite normally occurs on ears, nose, fingers, hands, toes and feet or other parts of the body that are left uncovered in below-freezing temperatures. Frostbitten skin becomes numb and turns a pale white color.
Hypothermia
Hypothermia occurs when a person's body temperature drops to or below 95° F. Common symptoms include bluish-colored skin, uncontrollable shivering and drowsiness or fatigue.
Avoid Cold-Induced Injuries and Illnesses
What to Do If Someone's Suffering from a Cold-Induced Injury or Illness
Insect Stings
Insect stings can be treated without medical attention unless the person suffers an allergic reaction.
The first step to treating an insect sting is to remove the stinger. This can be done by using a straight edge to scrape off the stinger or by using tweezers to pull it out. If you choose to use tweezers to remove the stinger, use extreme caution to not puncture the protruding venom sac.
After the stinger has been removed, a cold pack can be used during the first 24 hours to suppress pain and swelling. Following the first 24 hours, heat should be applied if pain or swelling persist.
Those with severe allergies to insect stings should consult a physician about carrying a prescription medical kit. The kit contains medicine and instructions to be used if the person is stung. If the kit is used, the victim still must receive medical attention. Call for help or take them to the nearest hospital.
Snake Bites
If you are bitten by a snake, seek medical attention immediately and try to describe the size and color of the snake to the doctor. This can help the doctor determine whether or not the snake was poisonous. Never cut, suck or apply cold packs to snake bites.
Mammals
Be aware of animals such as squirrels or bats that may be in trees or bushes and startle you during work. Also, be cautious of animals such as rats, skunks and raccoons that could be rabid.
Poison Ivy, Oak and Sumac
 |
Poison Ivy Leaves are usually found in clusters of three. |
Treating Cuts and Burns
Minor cuts and burns can be treated on the job site. Seek medical attention if:
Treating Cuts
Treating Burns
First Aid Kit Contents
The following is a list of minimum requirements for workplace first aid kits as outlined by ANSI Standard Z308.1-2003*.
*ANSI Z308.1-2003 is published by the International Safety Equipment Association, Arlington, VA www.safetyequipment.org Used with permission.
Quiz Yourself
Answers can be found here.
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
Tree trimming accidents can seriously injure or kill you. You have been presented with checklists, safety tips and exercises designed to help you avoid the most commonly reported causes of tree trimming injuries and deaths, as well as other important safety precautions to consider. Use this information to keep your work experience safe.
Quiz Yourself
Circle the correct answer. Answers can be found here.
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
Lesson 1
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
Lesson 2
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
Choose One: I am a __________ line-clearance tree trimmer.
Lesson 3
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
 f. Prusik Knot
f. Prusik Knot b. Bowline Knot
b. Bowline KnotLesson 4
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
Lesson 5
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
Conclusion
Circle the correct answer.
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
Publication #: MF2712
This material was produced under grant number 46G3-HT04 from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U.S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. government.
This booklet was produced by K-State Research and Extension, Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas.
The information in this publication has been compiled from a variety of sources believed to be reliable and to represent the best current opinion on the subject. However, neither K-State Research and Extension nor its authors guarantee accuracy or completeness of any information contained in this publication, and neither K-State Research and Extension or its authors shall be responsible for any errors, omissions, or damages arising out of the use of this information. Additional safety measures may be required under particular circumstances.
Brand names appearing in this publication are for product identification purposes only. No endorsement is intended, nor is criticism implied of similar products not mentioned.
Disclaimer and Reproduction Information: Information in NASD does not represent NIOSH policy. Information included in NASD appears by permission of the author and/or copyright holder. More