Introduction What's Inside?
Lesson 1 Take Control of Your Own Safety
Lesson 2 Working Safely Near Traffic
Lesson 3 Safety Starts Before the Engine
Lesson 4 Protect Yourself While Driving
Lesson 5 Operating Large Trucks
Lesson 6 Pulling Trailers
Lesson 7 Environmental Hazards
Conclusion
Quiz Yourself Solutions
This book teaches important safety practices for operating and working near motor vehicles. It is designed to use with your employer's safety training, the vehicle operator's manual, and your state driver's license manual. Information in this book reinforces safe operation of a motor vehicle in work-related situations.
1. Identify the leading cause of accidental death on the job.
2. Identify safe work habits operating motor vehicles.
Workers are more likely to be seriously injured or killed in incidents involving motor vehicles than from any other workplace hazard. The most commonly reported causes of job-related vehicle deaths and serious injuries are:
1. Being hit by traffic while working near a roadway.
Accident Report
Employee Killed At Intersection |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 125269456
An employee was working near a busy intersection when he was struck by an automobile. The driver of the automobile stated he did not see the employee. The employee was not using any reflective equipment or clothing; the worksite was not illuminated; and the highway warning signs were not displayed properly. The employee died at the scene.
 Protect yourself and your coworkers, use reflective equipment, clothing and warning signs Protect yourself and your coworkers, use reflective equipment, clothing and warning signs
|
2. Accidents at the job site.
Accident Report
Employee Ran Over By Truck |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 102919206
An employee was standing in a loading area occupied by several trucks. Another driver did not see him and backed a truck over him. The employee was killed.
 Check for coworkers and warn them before backing. Check for coworkers and warn them before backing.
|
3. Crashes driving to, from or between job sites.
Accident Report
Employee Killed In Fall From Pickup |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 112891445
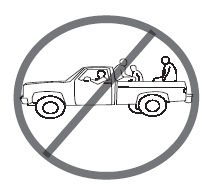
Two employees were riding home from work in the back of a coworker's pickup. One of the riders fell off the open tailgate and struck his head on the ground. He was killed.
 Never ride or transport passengers in the bed of a pickup. Never ride or transport passengers in the bed of a pickup.
|
|
| Never ride or transport passengers in the bed of a pickup. |
Safe work habits are important. Here are three actions you can take to be safe on the job site.
- Prepare for safe driving
You must have a valid driver's license to drive on public roads. Read the operator's manual for each vehicle you will be driving and know your company's driving policies.
- Concentrate on working safely
Whether you are the driver or a passenger, always wear your safety belt. Obey all traffic signs and signals. Risks and shortcuts can lead to serious injury and death.
- Additional Precautions
Do not operate machinery if you are tired or have taken drugs or alcohol. If you are on medication, discuss with your doctor or pharmacist if you are able to safely operate vehicles and machinery.
For answers, click here.
Use the list of words to complete the following sentences.
public roadway
drugs
incidents
safety belt
1. Motor vehicle ________________ are the leading cause of accidental death in the workplace.
2. When operating a motor vehicle you should always wear your _______________________.
3. To operate a motor vehicle on a __________________, you must have a valid driver's license.
4. Never operate a vehicle if you are under the influence of ______________ or alcohol.
1. Identify safety procedures to use when working on or near the shoulder of the roadway.
2. Recall how to use traffic control devices in your work zone.
From time to time your work site may be located near a road or street. Try to schedule jobs so you are not working in heavily traveled areas during morning and evening rush hours and at dusk or in darkness. Take steps to protect yourself, coworkers and equipment from traffic.
Accident Report
Employee Killed While Working in Median Strip |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 119565737
An employee was struck and killed by a car while working in the median. There were safety vests, traffic warning signs and safety cones in the company van, but the workers did not use any of them.
 Protect yourself and your coworkers, wear safety
vests, use traffic warning signs and safety cones. Protect yourself and your coworkers, wear safety
vests, use traffic warning signs and safety cones.
|
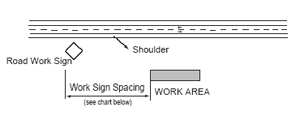
A temporary traffic control zone is an area where road user conditions are changed because of a work zone or an incident. Although each zone is different, the goal of your work should be to perform your work safely and with as little disruption to road users as possible.
Temporary traffic control devices such as warning signs and cones are placed in the zone. Their installation and maintenance should comply with the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD), http://mutcd.fhwa.dot.gov
The MUTCD covers three distinct work zones: construction, maintenance and utility work. To be effective, traffic control devices should meet five basic requirements:
- Fulfill a need
- Command attention
- Display a clear, simple meaning
- Command respect from road users
- Give adequate time for proper response
- Notify local police before starting a job that might interfere with traffic flow.
- All equipment, vehicles and materials should be stored away from traffic to avoid collision.
- Wear highly-reflective, brightly-colored vests and clothing to make yourself visible to traffic.
- Use highly-visible signs, cones and barricades to warn and direct traffic and protect you and your coworkers while working.
- All warning signs, cones and barricades should be easy-to-read and clean to maintain maximum visibility.
- Remove or cover warning signs when the job is finished or you are not working.
- When you must leave vehicles unattended, remember to roll up all windows, remove the keys and lock all the doors.
 If you will be working 60 minutes or less, a vehicle with activated high-intensity rotating lights may be used in place of a sign, cones and barricades. If you will be working 60 minutes or less, a vehicle with activated high-intensity rotating lights may be used in place of a sign, cones and barricades. |
When you are working beyond the shoulder, but within the
right-of-way, minimal traffic control is required. Generally, if
the work is 15 feet or more from the edge of the traveled way, or
two feet from the curb, no control devices are needed.
You should use a single warning sign when work lasts longer
than 60 minutes and when any of the following situations exist:
- Vehicles are parked on the shoulder
- Equipment is traveling on or crossing the roadway frequently
- Work is within 15 feet of the traveled way
- Work is within two feet of the curb
Appropriate warning signs for work beyond the shoulder include ROAD WORK AHEAD or SHOULDER WORK.
If you will be working 60 minutes or less, a vehicle with activated high-intensity rotating light may be used in place of a sign, cones and barricades.
Road Type |
Work Sign Spacing (ft) |
Urban
(40 mph or less) |
100 |
Urban
(45 mph or more) |
350 |
Rural |
500 |
Expressway |
1000 |
| To Find the Distance to the Sign |
| If you are working beyond the shoulder, you will only need one sign. Use the chart on the left to match the type of road you are working on to the distance (ft) in the first column. |
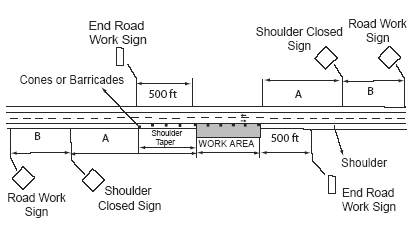
When you are closing a shoulder that is eight feet wide or more, you must add another warning sign. The general warning sign, such as ROAD WORK AHEAD should be used, followed by a SHOULDER CLOSED sign. You should also use cones and barricades to close the shoulder and direct traffic to remain within the traveled way. This is called a shoulder taper.
| To Find the Shoulder Taper |
Distance from the work area to the lead cone or barricade of the shoulder closure
width = width of one lane of traffic
speed = normal speed of road
For speeds of 45 mph or more: shoulder taper = width x speed ÷ 3
For speeds of 40 mph or less: shoulder taper = width x speed2 ÷ 60 ÷ 3
Example: If you are working on the shoulder of a highway with 10 ft lanes and a posted speed limit of 60 mph, the shoulder taper would be.....
10 x 60 ÷ 3 = 200 ft of shoulder taper
Example: If you are working on the shoulder of a highway with 10 ft lanes and a posted speed limit of 40 mph, the shoulder taper would be.....
10 x 402 ÷ 60 ÷ 3 = 89 ft of shoulder taper |
| How to Find the Distance Between Signs |
If you are working on the shoulder, you will need two signs to warn road users. Use the table to match the type of road with the distance you need between the signs.
|
Road Type |
Work Sign Spacing (ft) |
A |
B |
Urban (40 mph or less) |
100 |
100 |
Urban (45 mph or more) |
350 |
350 |
Rural |
500 |
500 |
Expressway |
1000 |
1500 |
For answers, click here.
1. Use the list of words below to complete the following sentences.
- Place warning signs far enough ahead of the work site so
drivers have time to react and _______________________
- Wear highly-reflective, brightly-colored _______________
when working near traffic.
- Keep ________________ away from the road so it will not
interfere with traffic flow.
- Whenever possible, plan to avoid working near busy roads
during ___________________________.
- If you are working ____________ the shoulder, only one
warning sign is required.
- When working on the shoulder, the shoulder __________ is
the distance from the work area to the lead cone or barricade
of the shoulder closure
1. Recall safe start up and shut down procedures of your vehicle.
2. Recognize how to safely park on hills.
Safe motor vehicle operation begins before you start the engine. You can help prevent accidents by performing a pre-start inspection of the vehicle and towed equipment. Alert your supervisor if you find anything wrong during your inspection.
Accident Report
Employee Injured When Brakes Fail |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 115171472
An employee was operating a dump truck when the brakes failed. The truck rolled backward down a hill, then off the roadway and over a steep bank. The employee was thrown from the vehicle and suffered severe injuries.
 Conduct a daily safety inspection. If something
is not working properly, alert your supervisor. Conduct a daily safety inspection. If something
is not working properly, alert your supervisor.
|
| Pre-Start Checklist |
 |
 |
Fuel and Fluid Levels |
 |
Tires |
 |
Safety Belts |
 |
Controls |
 |
Brakes |
 |
Windshields and Mirrors |
 |
Driver’s License |
Each day, check the vehicle you are using before start up.
Your inspection should include:
Fuel and Fluid Levels
Check the fuel gauge before you start. Periodically check oil, transmission, brake and washer fluid levels to make sure they meet your vehicle's operator's manual.
Tires
Walk around the vehicle and towed equipment and inspect the tires. Check tire pressure and look for signs of damage or excessive wear. Make sure lug bolts are tight.
Safety Belts
Make sure all safety belts are functioning, and everyone is properly restrained.
Controls
Check the horn to make sure it works. Test the lights, turn signals and windshield wipers before you begin.
Brakes
Make sure your brakes are working properly. Test according to your vehicle's operator's manual.
Windshields and Mirrors
Make sure the windshields and mirrors are clean. Adjust mirrors so you can see properly.
Driver's License
- Walk around the vehicle to make sure no people or obstacles are in your path.
- Buckle up before you start the engine. Wear a safety belt to reduce the risk of serious injury or death.
- Make sure the transmission is in park for automatic transmissions or neutral for standard transmissions. Most automatic vehicles will not start when the vehicle is in gear. For standard transmissions, make sure the parking brake is set and the transmission is in neutral, so the vehicle doesn't move.
- Adjust the seat, side and rear view mirrors. Adjust the seat so your feet reach the pedals, and your hands reach the steering wheel and controls. Adjust the seat so you have a clear line of sight through windows and mirrors as well.
Start the engine as recommended in the operator's manual.
Wear Your Safety Belt
Wearing your safety belt cuts your risk of being killed in a vehicle accident by half.
To provide protection, the lap portion of the safety belt must be worn low and snug across the hips, and the shoulder portion must be snug across the chest, away from the neck and face. Adjust your seat to ensure your safety belt is worn properly.
When it is time to shut down your vehicle you should:
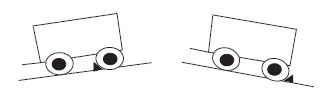
- Park on a level surface, if possible. If you have to park on a slope, you must adjust your front wheels to prevent the vehicle from rolling into traffic. If facing uphill with a curb, turn the wheels away from the curb. Otherwise, turn the wheels toward the curb or roadside. Always engage the parking brake.
- Secure the vehicle.
a. For automatic transmissions put the vehicle in park.
b. For standard transmissions put the vehicle in first gear or reverse and set the parking brake.
- Turn the engine off and remove the key from the ignition.
- Unbuckle your safety belt.
- Lock all doors and roll up windows before leaving the vehicle unattended.
 Always set the parking brake when parking on a hill. Always set the parking brake when parking on a hill. |
DOWNHILL
With or Without Curb |
UPHILL with Curb |
UPHILL Without Curb |
|
|
|
Turn Wheels TOWARD the Curb or Roadside |
Turn Wheels AWAY From the Curb |
Turn Wheels TOWARD the Roadside |
For answers, click here.
Use this list of words to complete the following sentences.
- Wearing your _______________________ cuts your risk of serious injury or death from a motor vehicle crash in half.
- Before driving, check the _______________________ levels.
- When a vehicle is facing downhill with or without a curb, turn the wheels ___________ the curb or roadside.
- When you must park on a slope, engage the ______________ so the vehicle will not roll.
- When a vehicle is facing uphill with a curb, turn the wheels _________________ the curb.
- As part of your _____________ pre-start safety inspection, inspect the tires on your vehicle and all towed equipment.
1. Recognize factors that contribute to motor vehicle crashes.
2. Identify ways to prevent crashes.
3. Interpret the meaning of traffic signs.
Safe driving means recognizing, assessing, and responding to potentially dangerous situations.
Accident Report
Employee Killed Driving to Job Site |
Summary of NIOSH FACE Report 91WY010
An employee was driving a company pickup to a work site. He had been working overtime and traveling between work sites the entire week. Halfway to his destination he ran into the back of a tanker truck and was killed. According to an accident investigation, no attempt was made to avoid hitting the tanker and distraction and fatigue led to the accident.
 Do not drive or operate equipment when fatigued. Avoid distractions while driving. Do not drive or operate equipment when fatigued. Avoid distractions while driving. |
- Driving over the speed limit or too fast for road conditions
- Being distracted
- Driving under the influence of alcohol, drugs or when fatigued
- Improper vehicle maintenance
Accident Report
Truck Driver Killed in Crash |
Summary of HWY-98-SH-003
A truck driver drove off a highway, struck a ditch embankment, became airborne, and landed on top of a stopped pickup. The truck driver and the two occupants of the pickup were killed. An investigation revealed the driver had been taking prescription pain medicine that made him drowsy.
 Do not operate a motor vehicle if you are using Do not operate a motor vehicle if you are using
prescription drugs that may cause impairment.
|
 Safety starts before the engine Safety starts before the engine |
Safe driving begins with you.
- Keep both hands on the steering wheel at all times.
- Be aware of what traffic around you is doing.
- Avoid other vehicle's blind spots.
- Obey all traffic signs and signals.
- Leave enough distance between you and the vehicle in front of you to stop safely.
Accident Report
Six Employees Injured In Accident |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 124815366
An employee was driving a van full of coworkers on a winding, downhill road. Despite his coworker's requests for him to slow down, he refused. The driver lost control and the speeding vehicle plunged more than 400 feet down a steep embankment. Four employees were ejected and had to be airlifted to a hospital were they were treated for serious injuries.
 Obey speed limits and drive slower in dangerous road conditions. Obey speed limits and drive slower in dangerous road conditions.
|
Speeding causes many motor vehicle crashes. Speed limits indicate the highest speed at which it is safe to drive on that road. You need to drive slower than the posted speed limit in poor weather or in dangerous road conditions. Always take into consideration the size and weight of a towed load.

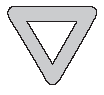
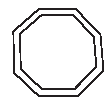
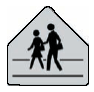
DIAMOND means General Warning
|

OCTAGON means Stop |

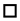
SQUARE means Traffic Regulations
|

RECTANGLE (long axis vertical) means Traffic Regulations |
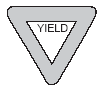
TRIANGLE means Yield |

PENNANT means No Passing |

CIRCLE means Railroad Crossing |

RECTANGLE (long axis horizontal) means Directional Information |

PENTAGON means Pedestrian Traffic |
When you are behind the wheel, your job as a driver requires full attention. Distractions slow your ability to respond to changing conditions. Distractions can be physical, mental, or both.
- Physical distractions require you to take your eyes off the road or remove your hands from the steering wheel. Examples of physical distractions include: adjusting vehicle controls, cell phone calls, eating and drinking. Designate a passenger to answer the phone or two-way radio or pull off the road and stop the vehicle before you begin the conversation. Adjust controls before you begin driving.
- Mental distractions take your focus off driving. Examples of mental distractions include conversations with passengers or on a cell phone, daydreaming, being frustrated, upset or otherwise distracted. Make an effort to clear your mind of distractions and concentrate on safe driving.
Research has proven that drivers who use cell phones in their vehicles have a higher risk of collision than drivers who do not. In addition, driving records revealed that cell phone users receive more traffic citations.
You will probably have days when driving conditions are poor because of the weather. Below are some tips for managing weather-related driving conditions.
Accident Report
Employee Crashes Into Tanker Truck And Semi |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 115165011
On an overpass, an employee's truck struck ice, skidded into a tanker truck, then collided with a semi-tractor head-on. The employee was not wearing his safety belt and died.
 Always wear your safety belt. Drive slower in Always wear your safety belt. Drive slower in
poor weather conditions.
|
Rain
- Slow down and allow extra space between you and the vehicle in front of you when driving on wet pavement.
- Use the windshield wipers.
- Use headlights on low beam to make your vehicle visible to other drivers and to help you see the road if it is dark. Low beams cause less reflection during rain.
- Do not drive in standing or flowing water. Your vehicle could be swept away by the water or the engine could stall, leaving you stranded.
Snow/Ice
- Scrape snow and ice from windshield for better visibility.
- Drive slower and increase following distance. Even snow tires slide on ice or packed snow.
- Watch for slick spots on bridges and overpasses.
Fog
- Turn headlights on low beam and use fog lamps, if available.
- Fog decreases your visibility. Drive slower and increase following distance.
Wind
- Increase your following distance so you have time to react to events around you, such as objects blowing across the road or the vehicle in front of you slowing or stopping suddenly.
- Keep both hands firmly on the steering wheel, so you maintain control of the vehicle.
- Be cautious when pulling a trailer in the wind. The wind will push and tug at the trailer making driving difficult.
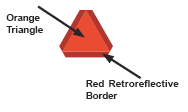
A vehicle that cannot travel over 25 mph must display a Slow Moving Vehicle (SMV) emblem. The SMV emblem is an orange triangle (visible in daylight) with a red retroreflective border (visible at night). It is a universal symbol indicating the vehicle is moving at 25 mph or slower. An SMV emblem does not replace other vehicle warning devices such as tail lights, flashers or reflectors. The SMV emblem must be visible from at least 600 feet from the rear of the vehicle or towed equipment. The mounting height may vary from 2 to 10 feet above the road surface with the point of the triangle up. Never display an SMV emblem on a vehicle or trailer that will be moving faster than 25 mph.
- Always signal when making a lane change
- Before changing lanes, check the mirrors and look for vehicles
- Obey all posted traffic signs, signals and pavement markings
Pavement markings indicate:
- Where on the roadway you should drive
- Passing and no passing zones
- Road edges
Pavement marking colors:
- YELLOW lines divide 2-way traffic
- WHITE lines divide same way traffic
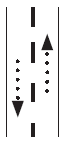 Two-way traffic, passing permitted.
Two-way traffic, passing permitted. |
|
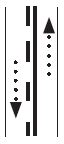 Two-way traffic. Passing permitted in lane with dashed line.
Two-way traffic. Passing permitted in lane with dashed line. |
|
|
|
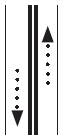 No passing either direction.
No passing either direction. |
|
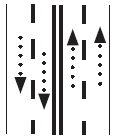 Multi-lane, two-way road.
Multi-lane, two-way road. |
|
Never drive while fatigued or under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
- Alcohol and drugs affect your ability to think clearly and react quickly. Prescription and nonprescription drugs may affect your driving. Ask a pharmacist or doctor if your medicine will affect your ability to drive and operate machinery.
- Fatigue affects your safety and can put others in danger. Make sure you get adequate rest before work.
- Take short breaks frequently, especially if you are driving or seated for extended periods of time. Stand up, stretch, walk around or get something to drink. Any activity will help refresh you.
Accident Report
Employee Crashes Into Tanker Truck And Semi |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 115158206
An employee lost control of the vehicle she was driving and was killed. She had an elevated blood alcohol level. She was exceeding the speed limit and not wearing her seat belt at the time of the accident.

|
For answers, click here.
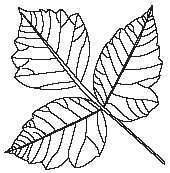
- Match the traffic sign with its meaning.
| Stop |
|
| Pedestrian Traffic |
|
| No Passing |
|
| Yield |
|
- Use this list of words to complete the following sentences.
- To avoid distractions, do not answer cell phone calls while ___________________.
- Always signal when making a _______________________.
- Always display an SMV emblem on a vehicle or trailer that cannot travel _________________ 25 mph.
- Identify safe loading and unloading procedures.
- Recognize safe operating procedures when driving big trucks.
Fully loaded trucks are slower and more difficult to steer than passenger vehicles. Hauling heavy loads to and from job sites requires special training and knowledge.
Accident Report
Employee Dies In Crash At Job Site |
Summary of FACE Report 92-19
An employee was driving a large water tank truck on a job site. His truck and another vehicle approached head-on. The employee swerved, but hit the front tire and fender of the other vehicle. His truck overturned and the employee died. He was not wearing his safety belt.
 Large trucks can overturn easily. Always fasten your safety belt. Large trucks can overturn easily. Always fasten your safety belt.
|
- Load and unload on a level surface.
- Use wheel blocks to keep the truck from moving during loading and unloading.
- Do not overload the truck. An overloaded truck is harder to steer and stop. Heavy loads also put additional stress on tires, brakes, suspension, the cooling system and the drive train. Look for load limits on the truck's data plate and operator's manual.
- Be careful loading high-profile cargo. Make sure cargo will not hit overhead power lines, highway overpasses or bridges.
Accident Report
Worker Backed Over By Dump Truck |
Summary of FACE Report 2002-06
A loaded dump truck entered a work zone. The driver positioned the truck so he could back up to unload. He saw a coworker standing near his unloading site. He believed the worker had moved, and began backing up. The worker had not moved, and was killed when the dump truck ran over him.
 Know where your coworkers are before moving trucks and motor vehicles. Know where your coworkers are before moving trucks and motor vehicles.
|
- Have a valid driver's license or a Commercial Driver's License (CDL) if necessary. Follow licensing laws for your state.
- Allow extra space between you and the vehicle in front of you. Also allow extra time to pass. A loaded truck takes longer to accelerate to highway speed and longer to stop. Watch for cars pulling out in front of you and be ready to react.
| Did You Know? |
 It takes about twice the distance to stop a heavy truck as it does a passenger vehicle traveling at the same speed. It takes about twice the distance to stop a heavy truck as it does a passenger vehicle traveling at the same speed. |
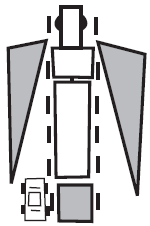
- Be aware of blind spots, especially when turning and making lane changes. Big trucks have blind spots: directly in front, on either side and directly behind the truck. The size of the blind spot varies with the size of the truck.
- Be aware of where coworkers are before moving.
Accident Report
Worker Backed Over By Dump Truck |
Summary of FACE Report 2002-06
A loaded dump truck entered a work zone. The driver positioned the truck so he could back up to unload. He saw a coworker standing near his unloading site. He believed the worker had moved, and began backing up. The worker had not moved, and was killed when the dump truck ran over him.
 Know where your coworkers are before moving trucks and motor vehicles. Know where your coworkers are before moving trucks and motor vehicles.
|
- Use the horn to indicate when you are backing unless the truck is equipped with an automatic back up alarm.
- Know the characteristics of the load you are carrying.
- Make sure high profile loads will not contact overhead power lines, bridges or overpasses.
- Materials such as gravel or dirt may shift during turns causing the truck to become out of balance and tip over.
- Liquids carried in a tank will shift if the tank is not full, making it difficult to control the vehicle.
- Indicate oversized loads with signs. Signs are normally placed on the back of any load that extends beyond the end of the truck or is wider than the truck bed. Follow your state's laws for marking oversized loads.
- Never carry people in the cargo area of the truck. They can fall or be thrown.
- Set the parking brake when the truck is parked so it will not roll. If you have to park on a slope, you must also adjust your front wheels to prevent the vehicle from rolling into traffic. If facing uphill with a curb, turn the wheels away from the curb. Otherwise, turn the wheels toward the curb or roadside. Always engage the parking brake.
| Did You Know? |
 Federal, state, and local regulations for vehicle weight, securing cargo, covering loads, and where you can drive large vehicles vary. Know the rules where you will be driving. Federal, state, and local regulations for vehicle weight, securing cargo, covering loads, and where you can drive large vehicles vary. Know the rules where you will be driving. |
Accident Report
Employee Crushed Between Truck Bed and Frame |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 000729756
An employee raised the bed of a 2-ton dump truck to add hydraulic fluid to the reservoir. He did not use a lift support to secure the bed. While he was adding hydraulic fluid, the bed fell and crushed him to death. A lift support device was available, but he had chosen not to use it.
 Never work under a raised, unsupported,
truck bed. Always use lift support. Never work under a raised, unsupported,
truck bed. Always use lift support.
|
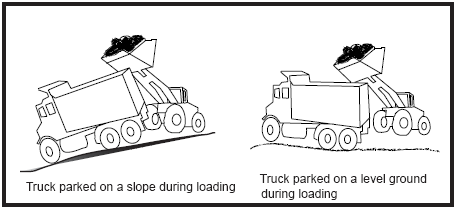
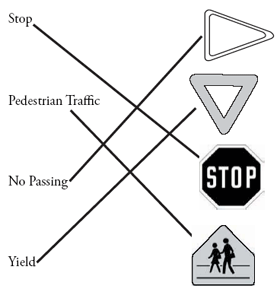
- Only raise the bed with the truck parked on level ground. A raised bed increases the truck's center of gravity. Side overturns are common on sloped ground or when the truck is turning with the bed raised.
- Check for clearance before raising the bed and dumping. Be aware of the location of overhead wires, obstructions and people when dumping. When necessary, have a coworker direct you to the unloading area.
Accident Report
Employee Crushed Between Truck Bed and Frame |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 103303095
An employee was trying to repair a control link on the hydraulic lift of a dump truck. He raised the bed of the truck and placed his head and neck between the rails on the body and the truck frame. He had not blocked the bed in the raised position and it fell across his head and neck. He was killed.
 Never put any part of your body between the truck frame and a raised bed, unless a lift support has been installed. Never put any part of your body between the truck frame and a raised bed, unless a lift support has been installed.
|
- Always block the empty truck bed with an approved lift support before putting any part of your body between the truck body and frame. The e dumping mechanism operates on hydraulics and there is always a potential for failure.
- If the truck bed gets stuck up and won't come down
- Set the brakes
- Turn off the engine
- Remove the key from the ignition
- Block the bed before attempting to work on the truck.
|
|
Never work under a raised bed without an approved lift support. |
Always block the empty
bed before inspection or
maintenance. |
| Safe Dumping Checklist |
 |
Park on Level Ground |
 |
Set the Parking Brake |
 |
Put Truck in Park or Neutral |
 |
Check for Clearance |
 |
Observe all PTO Safety Instructions |
 |
Raise Bed Slowly |
 |
Brace an Empty Raised Truck Bed |
 |
Lower Bed Slowly |
For answers, click here.
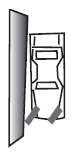
- For the following drawing, choose the drawing that shows the truck driver working correctly.
- Use the list of words below to complete the following sentences.
block
parked
heavy load
failure
truck
- Because there is always a potential for hydraulic __________ , block a raised truck bed with an approved device.
- When the truck is ____________, set the parking brake.
- A _________________________ puts extra stress on the truck's tires, suspension, cooling system, and drive train.
- A loaded _____________ takes longer to reach highway speed and longer to stop. e. When working on a truck with a raised bed, always _______ the bed with an approved lift support device.
- Recall how to safely hitch and unhitch a trailer.
- Interpret safe trailer loading procedures.
Driving a vehicle with a trailer attached requires special training and knowledge. Before towing a trailer on the job, you should receive hands-on training to understand how the vehicle handles with an attached trailer.
Accident Report
Employee Ran Over By Trailer |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 119901858
An employee pulled the wheel blocks from a tow truck and trailer so the driver could pull forward. After the driver pulled the trailer ahead, he discovered the employee lying on the ground. He had been in the driver's "blind spot" and was ran over by the trailer.
 Always check your blind spots and warn your coworkers before moving trailers. Always check your blind spots and warn your coworkers before moving trailers.
|
- Check the operator's manual to make sure the towing vehicle is capable of pulling the load before you attach a trailer. The operator's manual for the tow vehicle and trailer will list the vehicle and trailer's towing weight limits. Weight limit information may also be found on the trailer's data plate.
- Stabilize the trailer before hitching by blocking the wheels so it does not accidentally roll over someone.
- Hitch and unhitch on level surfaces so the trailer does not roll.
- Make sure the trailer is properly hitched to the towing vehicle. Follow the directions in the operator's manual.
- Always attach safety chains and fasten lighting connectors. The safety chain must be strong enough to hold the trailer securely if the primary hitch fails.
- Check the brake and signal lights on the trailer before driving.
- To prevent rolling, stabilize the trailer before unhitching by blocking the wheels. Place the blocks in the direction the trailer is most likely to roll. When you are unsure which way it might roll, block both front and rear wheels.
|
Block in the direction the trailer is most likely to roll.
If in doubt, block both wheels. |
- Lock the parking brake on the towing vehicle before loading or unloading the trailer.
- Block the trailer wheels before loading or unloading.
- Do not overload the trailer. Overloading makes it more difficult to steer the towing vehicle and may cause the engine to overheat. Loads also increase pressure on tires. Load limits are posted on the equipment or in the owner's manual.
- Use the trailer jack when loading a trailer that is not attached to the towing vehicle. The trailer could tip forward if the tongue is not supported.
- Balance weight from side to side and front to back. Too little weight on the trailer tongue can cause the vehicle to sway. Too much tongue weight can cause steering problems.
- Secure loads to the trailer.
- Make sure loads will not contact overhead power lines, bridges, or overpasses.
- Know the legal width and height limits for the road you are traveling on before you begin.
- Indicate oversized loads with a sign. Check your state laws for specific marking requirements. Normally highly-visible "wide load" signs on the front of the tow vehicle and the back of the trailer are required.
- Indicate extra long loads by using a highly-visible sign on the back of any load that extends beyond the end of the trailer.
- Keep bystanders at a safe distance during loading and unloading. Know where others are before you pull the trailer away from the loading/unloading area.
Accident Report
Employee Riding In Trailer Injured, Killed |
Summary of OSHA Accident Inspection 114987746
Three employees were riding in a trailer being towed by a tractor, when the trailer was struck by a passenger car. Two employees were thrown from the trailer and killed instantly. The third jumped from the trailer and broke his back.

|
- Never carry people in a towed trailer.
- Adjust the mirrors on the towing vehicle so you can see the end of the trailer.
- Be aware of "blind spots" in mirrors, especially when turning and making lane changes.
|
Be aware of blind spots.
The shaded areas show "blind spots", where vehicles can disappear from your vision. |
- Use moderate speeds on the highway. Adjust speed to correspond with length and weight of trailer load. Drive slower to reduce strain on towing vehicle and trailer.
- Avoid sudden stops and starts that can cause the trailer to skid, slide or jackknife.
- Allow more distance for stopping because of the trailer's extra weight.
- Drive slower on rough roads, railroad crossings or when driving through ditches.
- When passing, allow extra distance to clear the vehicle before pulling back into your lane.
- Don't drive on soft shoulders. This could cause the trailer to jackknife or you to lose control.
- Make wider turns at corners. The trailer's wheels are closer to the inside of the turn than the wheels of the towing vehicle so they are more likely to hit curbs.
- Make sure high profile loads will not contact overhead power lines, bridges or overpasses.
- Ask another worker to guide you when backing the trailer.
For answers, click here.
- Use the list of words below to complete the following sentences.
over load
weight
level
safety chains
- Hitch and unhitch on ______________________ ground.
- Always attach ______________________ and fasten lighting connectors when hitching a trailer to the tow vehicle.
- Balance __________________________ on a trailer from side to side and front to back.
- Do not ___________________________ the tow vehicle or the trailer.
- Identify environmental hazards.
- Recognize treatment and first aid for exposure to environmental hazards.
You can become seriously ill or die if you do not take the proper precautions while working in high temperatures and humidity. Heat can reduce physical performance, as well as mental alertness, causing more accidents.
Heat Facts
- You are more likely to suffer from a heat related illness on humid days.
- If you are not used to working in the heat, you are more likely to suffer from a heat related illness. It can take your body anywhere from 5 days to 2 weeks to be acclimated to working in the heat. It is recommended that new workers who begin in hot, humid weather, start out by working half of the normal time and workload on the first day and then build up to a complete day by the end of the week.
- You are more vulnerable to heat illness if you have suffered in the past.
- During the course of the day, you can produce as much as 2 to 3 gallons of sweat. Replenish this fluid by drinking liquids so that you do not suffer from a heat related illness.
- If someone feels overheated, move them into a cooler, preferably air conditioned area. Watch the person and seek medical attention if needed.
- Fan the person in order to increase cooling.
- Have the person drink plenty of fluids.
- If the person goes into convulsions or shows symptoms of heat stroke, call 911 immediately and take steps to cool them down such as soaking their clothing in cool water.
Heat Exhaustion Symptoms
Heat exhaustion is a serious illness and needs to be treated immediately before a heat stroke occurs. If you or a coworker experience any of the following symptoms, cool off immediately and drink plenty of water.
- Dizziness
- Light headedness
- Headache
- Feeling weak, fatigued
- Clammy and moist skin
|
Heat Stroke Symptoms
Heat Stroke is a medical emergency that can become fatal. If anyone experiences the following symptoms of heat stroke, call 911 immediately.
- Hot, dry, red skin (not sweaty)
- Disorientation
- Confusion
- Body temperature greater than 105° F
- Convulsing
- Unconsciousness
|
It is important to keep yourself hydrated and cool while working outside.
- Drink water often throughout the day; don't wait until you're thirsty to get a drink. At least a quart of water per hour is recommended.
- Stay away from soda, coffee, tea and alcoholic drinks that dehydrate the body.
- Avoid large meals before working in the heat.
- Some prescriptions can make you more susceptible to heat illnesses. Check with your doctor or pharmacist to see if any medicine you are taking could affect you while working in the heat.
- Wear light-weight fabric, such as cotton, to help keep your body cool.
- Wear a hat or sun visor on sunny days to help control body temperature.
- Plan to do the heaviest work at the coolest part of the day. This is usually between 6 a.m. and 10 a.m.
- Take frequent, short breaks in shaded areas to cool down.
- Do not take salt tablets, unless recommended by your doctor. Most people receive enough salt in their diet to account for the salt that is lost through sweating.
Prolonged exposure to sunlight causes skin cancer, cataracts and other serious illnesses.
- Choose a sunscreen that is marked broad-spectrum. This will protect you from both UVA and UVB rays. Ensure the Sun Protection Factor (SPF) is at least 15.
- Wear a hat or sun visor, sunglasses, and lightweight long-sleeve shirts and pants on sunny days to help control body temperature and block the sun.
Lightning strikes injure and kill hundreds of people each year. Follow these precautions to help keep you safe when the weather turns bad.
- As soon as you hear thunder, shut off and put away equipment and move indoors out of the storm. When you are able to hear thunder, you are able to be struck by lightning. Lightning can strike even when it's not raining.
- The cab of an enclosed vehicle provides some protection from lightning but a sturdy building provides the best protection.
- Listen to the radio for weather updates and storm warnings.
- Get to a low space. Lightning strikes the tallest objects.
- Crouch down on the balls of your feet. Place your hands on your knees and lower your head between your knees.
- Minimize contact with the ground.
- Do not lie flat on the ground. This will make you a larger target.
- Large, lone trees and towers, fences, telephone poles and power lines.
- Rivers, lakes, pools and other bodies of water.
- Metal objects, tools, equipment, wire fences and umbrellas.
- Call 911
- Check to see if they're breathing. Rescue breathing or CPR may be required.
- Check for burns on their body.
- Move the victim inside, out of the storm.
- Note: Most lightning-strike victims survive with immediate treatment and rescue breathing or CPR.
| Lightning Facts |
 |
A person that is struck by lightning DOES NOT retain an electric charge that can shock you. |
 |
Lightning can spread as far as 60 feet after striking the ground. |
 |
Lightning can travel at speeds of 100,000 mph. |
 |
The temperature of a bolt of lightning can be as high as 50,000° F. |
 |
Lightning CAN strike the same place twice. |
Prolonged exposure to freezing temperatures can result in cold induced injuries and illnesses that can seriously injure or kill you.
Cold temperatures reduce mental alertness and cause fatigue and exhaustion that can lead to accidents.
Frostbite
Frostbite occurs when parts of the body become so cold that the skin and tissue freezes. Frostbite normally occurs on ears, nose, fingers, hands, toes and feet or other parts of the body that are left uncovered in below-freezing temperatures. Frostbitten skin becomes numb and turns a pale white color.
Hypothermia
Hypothermia occurs when a person's body temperature drops to or below 95° F. Common symptoms include bluish-colored skin, uncontrollable shivering and drowsiness or fatigue.
Avoid Cold-Induced Injuries and Illnesses
- Layer clothing when working in cold temperatures; you can easily take off layers if you are too warm.
- Wear a hat and gloves.
- Keep muscles warm and loose by moving as much as possible.
- Take frequent, short breaks in warm areas.
- Perform work at the warmest part of the day, typically in the afternoon.
- Never work alone.
What to Do If Someone's Suffering from a Cold-Induced Injury or Illness
- Move the person out of the cold and into an area that is warm and dry.
- Remove wet and tight clothing and cover the person with a blanket.
- Never rub the affected area. This will cause further skin and tissue damage.
- Seek medical attention immediately.
Insect stings can be treated without medical attention unless the person suffers an allergic reaction.
The first step to treating an insect sting is to remove the stinger. This can be done by using a straight edge to scrape off the stinger or by using tweezers to pull it out. If you choose to use tweezers to remove the stinger, use extreme caution to not puncture the protruding venom sac.
After the stinger has been removed, a cold pack can be used during the first 24 hours to suppress pain and swelling. Following the first 24 hours, heat should be applied if pain or swelling persist.
Those with severe allergies to insect stings should consult a physician about carrying a prescription medical kit. The kit contains medicine and instructions to be used if the person is stung. If the kit is used, the victim still must receive medical attention. Call for help or take them to the nearest hospital.
If you are bitten by a snake, seek medical attention immediately and try to describe the size and color of the snake to the doctor. This can help the doctor determine whether or not the snake was poisonous.
Never cut, suck or apply cold packs to snake bites.
Be aware of animals such as squirrels or bats that may be in trees or bushes and startle you during work. Also, be cautious of animals such as rats, skunks and raccoons that could be rabid.
- Wash the affected area and all clothing and tools that may have touched the plant.
- Avoid scratching the area if possible, to prevent infection.
- Hot and cold compresses can be used to suppress itching.
- Consult a doctor if the rash is on the face, inside the mouth or covers a large portion of the body.
 |
Poison Ivy Leaves are usually found in clusters of three. |
Minor cuts and burns can be treated on the job site.
Seek medical attention if:
- Cuts are severely bleeding, more than one-half inch long and one-quarter inch deep, or the result of a puncture wound.
- Burn area covers more than one-fifth of the body with blisters, blisters occur on the hands, feet, face or genitalia, or if the skin is blackened or charred.
Treating Cuts
- Clean the area thoroughly.
- Remove any debris that may be in the wound.
- Apply pressure to the wound using gauze or a clean, absorbent cloth until the bleeding stops. If blood seeps through the cloth, do not remove it, continue adding more gauze or cloth over the previous one.
- Apply an antibiotic ointment and cover with a bandage or clean gauze.
- Allow wound to heal and keep dirt from creating infection by changing the bandage or gauze frequently.
- If a limb has been amputated, elevate while applying direct pressure and call 911.
Treating Burns
- Cool the burn by placing it under cool running water or in a container of cool water for at least 15 minutes.
- Cover the area with gauze or a clean cloth.
- Allow burn to heal and keep dirt from creating infection by changing the gauze frequently.
- If blisters occur, do not break them. Cover with gauze and allow them to break on their own.
The following is a list of minimum requirements for workplace first aid kits as outlined by ANSI Standard Z308.1-2003*.
- absorbent compress
- adhesive bandages
- adhesive tape
- individual-use antiseptic applications
- individual-use burn treatment applications
- latex-free medical exam gloves
sterile pads
- triangular bandage
*ANSI Z308.1-2003 is published by the International Safety Equipment Association, Arlington, VA www.safetyequipment.org. Used with permission.
Choose the correct answer.
For answers, click here.
- Stop a cut from bleeding by applying ______________.
- Aloe
- Ointment
- Direct pressure
- Dizziness, light headedness, headache and fatigue are all symptoms of _____________.
- Lightning strike
- Heat exhaustion
- It is important to take frequent, short _________ when working outside.
- Strides
- Phone calls
- Breaks
- To keep myself hydrated when working outside, I should drink __________.
- Water frequently throughout the day
- Only when I'm thirsty
- Soda at lunchtime
- Lightning strikes the ________ objects.
- Tallest
- Widest
- Shortest
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
- Immediately
- Stinger
- Wash
- Frostbitten
- Lower
- Never rub and area that has been _____________.
- The first step to treating an insect sting is to remove the _____.
- If you contact poison ivy, oak or sumac, ______ the affected area as well as all clothing and tools.
- Hypothermia occurs when body temperature drops to 95° or ___________.
- If a person with a known allergy to insects is stung, call for help ___________________.
Vehicle crashes are the leading cause of death on the job site. Take charge of your own safety. Prepare for safe driving by knowing how to operate your vehicle. Read the operator's manual and ask questions. This booklet has presented you with safety tips and exercises designed to help you avoid the most commonly reported types of job related motor vehicle accidents. Use this information to keep your work experience safe.
For answers, click here.
Use the list of words to complete the following sentences.
driver's
license
block
stress
always
- When operating a motor vehicle you should ______________ wear your safety belt.
- To operate a motor vehicle on a public roadway, you must have a valid __________________.
- A heavy load puts extra ____________ on the truck's tires, suspension, cooling system, and drive train.
- When working on a truck with a raised bed, always ________ with an approved lift support device.
Use the list of words to complete the following sentences.
- Motor vehicle incidents are the leading cause of accidental death in the workplace.
- When operating a motor vehicle you should always wear your safety belt.
- To operate a motor vehicle on a public roadway , you must have a valid driver's license.
- Never operate a vehicle if you are under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
- Use the list of words below to complete the following sentences.
- Place warning signs far enough ahead of the work site so drivers have time to react and slow down .
- Wear highly-reflective, brightly-colored clothing when working near traffic.
- Keep equipment as far away from the road so it will not interfere with traffic flow.
- Whenever possible, plan to avoid working near congested trafficways during rush hours.
- If you are working beyond the shoulder, only one warning sign is required.
- When working on the shoulder, the shoulder taper is the distance from the work area to the lead cone or barricade of the shoulder closure
Use this list of words to complete the following sentences.
- Wearing your safety belt cuts your risk of injury or death from a motor vehicle crash in half.
- Before driving, check the fuel and fluid levels.
- When a vehicle is facing downhill with or without a curb, turn the wheels toward the curb or roadside.
- When you must park on a slope, engage parking brake so the vehicle will not roll.
- When a vehicle is facing uphill with a curb, turn the wheels away from the curb or roadside.
- As part of your daily pre-start safety inspection, inspect the tires on your vehicle and all towed equipment.
- Match the traffic sign with its meaning.
- Use this list of words to complete the following sentences.
- To avoid distractions, do not answer cell phone calls while driving.
- Always signal when making a lane change.
- Always display an SMV emblem on a vehicle or trailer that cannot travel over 25 mph.
- For the following drawing, circle the drawing that shows the truck driver working correctly.
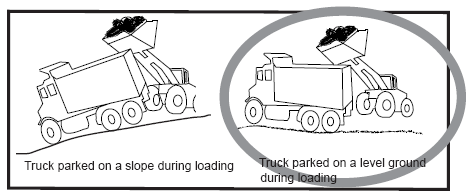
- Use the list of words below to complete the following sentences.
- Because there is always a potential for hydraulic failure, block a raised truck bed with an approved device.
- When the truck is parked, set the parking brake.
- A heavy load puts extra stress on the truck's tires, suspension, cooling system, and drive train.
- A loaded truck takes longer to reach highway speed and longer to stop.
- When working on a truck with a raised bed, always brace the bed with an approved lift support device.
- Use the list of words below to complete the following sentences.
- Hitch and unhitch on level ground.
- Always attach safety chains and fasten lighting connectors when hitching a trailer to the tow vehicle.
- Balance weight on a trailer from side to side and front to back.
- Do not over load the tow vehicle or the trailer.
Choose the correct answer.
- Stop a cut from bleeding by applying ______________.
- Aloe
- Ointment
- Direct pressure
- Dizziness, light headedness, headache and fatigue are all symptoms of _____________.
- Lightning strike
- Heat exhaustion
- It is important to take frequent, short _________ when working outside.
- Strides
- Phone calls
- Breaks
- To keep myself hydrated when working outside, I should drink __________.
- Water frequently throughout the day
- Only when I'm thirsty
- Soda at lunchtime
- Lightning strikes the ________ objects.
- Tallest
- Widest
- Shortest
Select the correct answer for the following sentences from the list below.
- Immediately
- Stinger
- Wash
- Frostbitten
- Lower
- Never rub and area that has been d. Frostbitten.
- The first step to treating an insect sting is to remove the b. Stinger.
- If you contact poison ivy, oak or sumac, c. Wash the affected area as well as all clothing and tools.
- Hypothermia occurs when body temperature drops to 95º or e. Lower.
- If a person with a known allergy to insects is stung, call for help a. immediately.
- Use the list of words to complete the following sentences.
- When operating a motor vehicle you should always wear your safety belt.
- To operate a motor vehicle on a public roadway, you must have a valid driver's license .
- A heavy load puts extra stress on the truck's tires, suspension, cooling system, and drive train.
- When working on a truck with a raised bed, always block or brace with an approved lift support device.
Publication #: MF2709
This material was produced under grant number 46G3-HT04 from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U.S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. government.
This booklet was produced by K-State Research and Extension, Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas.
The information in this publication has been compiled from a variety of sources believed to be reliable and to represent the best current opinion on the subject. However, neither K-State Research and Extension nor its authors guarantee accuracy or completeness of any information contained in this publication, and neither K-State Research and Extension or its authors shall be responsible for any errors, omissions, or damages arising out of the use of this information. Additional safety measures may be required under particular circumstances.
Brand names appearing in this publication are for product identification purposes only. No endorsement is intended, nor is criticism implied of similar products not mentioned.
Disclaimer
and Reproduction Information: Information in NASD does not
represent NIOSH policy. Information included in NASD appears
by permission of the author and/or copyright holder. More
Disclaimer and Reproduction Information: Information in
NASD does not represent NIOSH policy. Information included in
NASD appears by permission of the author and/or copyright holder.
More