Contents
Introduction
What's Inside?.
Training Techniques.
Tractor Safety Training Guide.
Motor Vehicle Safety Training Guide.
Chipper/Shredder Safety Training Guide.
Skid Steer Safety Training Guide.
Tree Trimming Safety Training Guide.
Aerial Lift Safety Training Guide.
Mowing and Trimming Safety Training Guide.
Aerial Lift Safety Training Guide
Suggested Materials
- Aerial Lift Safety Manuals (English, Spanish)
- Sign-in Sheet
- Pencils
- Instructor Guide
- Training Overheads/Slides/Projector
- Blank Overheads/Flipchart/Blackboard/Pen for listing participant responses and outlining important concepts.
- Ear Plugs and other appropriate protective equipment for Hands-on Exercises
- Fall protection equipment (lanyard, harnesses, etc.)
- First Aid Kits for Hands-on Exercises
- Aerial Lift Truck for Hands-on Exercises
- Temporary Traffic Control Devices for Hands-on Exercises
- Other equipment appropriate for Hands-on Exercises (chainsaws, pole saws, etc.)
Sources of Background Information
Aerial Lift and Tree Trimming Safety Manuals available for download: http://www.oznet.ksu.edu/agsafe/training/OSHA_training.htm
Operator's manuals for aerial lifts (available from dealer)
Length of Time Needed for Training
Review and select the learning activities that are most appropriate. If all of the discussion and hands-on exercises are included in the training it may take up to a full work day. Without the hands-on exercises, the classroom portion will take about two hours.
Welcome and Introduction
- Introduce yourself.
- Remind participants of the topic of the training.
- Discuss breaks, locations of restrooms, ending time and any tests or evaluations.
- Tell participants you expect them to play an active role by relating their experiences and knowledge.
Participant Introductions
Find out:
- Who are they?
- What is their experience with aerial lifts?
- What do they hope to learn from the training?
Questioning/Discussion
Before beginning Lesson 1:
- What do participants think are the most common types of accidents that involve aerial lifts? List ideas on an overhead or flipchart.
- Have any participants known someone who has been killed or seriously injured in an aerial lift accident? Would anyone care to share what happened?
Lesson 1 Take Control of Your Own Safety
Suggested Objectives
- Name the most common types of accidents involving aerial lift devices.
- Interpret the meaning of common warning signs and labels.
- Identify appropriate protective equipment.
Discuss Accident Reports on pages 4 -5 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual
- Refer to the list of participants' ideas about the most common causes of accidents. How well do participant's ideas match the actual causes of death?
- Are participants surprised by any of the most common types of accidents?
Hands-on Exercise
- Divide the class into groups of three to five participants. Have each group look for safety messages and signs on equipment they commonly use (aerial lifts, chain saws, pole saws, etc.). Bring the class together and ask each group to report on the hazards described in the messages and signs they saw.
- Have participants inspect and wear any protective equipment that is required for their work. Discuss the importance of each item.
- Practice wearing hearing protection:
- Follow manufacturer's procedure or use the general procedure below.
- Demonstrate technique.
- Provide feedback as participants practice.

Inserting Ear Plugs
Types of Hearing Protection
| Ear Plugs |
 |
- Clean hands.
- Roll ear plug between fingers to compress it.
- Grasp ear from behind your head with opposite hand and pull up to straighten ear canal.
- Insert ear plug until it blocks sound, then hold in place while it expands. (Count out loud to 20 while it expands.)
- Ear plug must completely fill ear canal.
- Test fit by cupping hands over ears and then releasing. There should not be much difference in sound.
- Wash reusable plugs in warm soapy water after use/throw away disposable after each use.
|
| Hearing Bands |
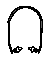 |
- Grasp ear from behind your head with opposite hand and pull up to straighten ear canal.
- Use your hands to press the ear pads into the ear canals.
- Test fit in a noisy environment: Lightly press band inward and you should not notice much reduction in noise level.
|
| Ear Muffs |
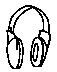 |
- Make sure the cushions fully cover the ear and seal tightly against the head.
- Hold the headband at the crown of the head and adjust each cup.
- Test fit in a noisy environment: Gently push the cups toward your head and release. There should not be much difference in noise level.
|
Evaluation
Answer the quiz items on page 8 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual individually or as a class. Be sure to discuss each item.
Questioning/Discussion
Before beginning Lesson 2:
- What specific safety items do participants check in regard to their equipment and worksite before beginning each job? List responses on an overhead or flipchart.
- What precautions do they take when they shut down their equipment and leave it unattended?
Lesson 2 Prepare for Safe Operation
Suggested Objectives
- Indicate parts to be inspected before operation.
- Recognize safe start up, shut down and operating procedures.
- Identify guidelines for working near traffic.
Discuss the Pre-Start Inspection and Checklist on pages 9 -10 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual
- How do the checklist items compare with the list made by participants at the end of Lesson 1.
- Discuss your company's policy for recording pre-operation equipment checks.
- Discuss the safety features that are present on your company's aerial lift trucks. Why are these important?
- Discuss your company's policy for safety belt use.
- Discuss your company's practices for communication between the person on the lift and those on the ground.
Analysis
On pages 10-11 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual, have each participant read one of the following items and briefly give an example of how an accident could occur if the procedure isn't observed.
- Items 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 under "Start Up Safety Procedures"
- Items 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 7 of "Safe Shut Down Procedures"
- All bullets under "General Operating Procedures"
Visual Aid
Display and discuss the overhead/slide entitled, "Is This a Good Idea?" on page 181 of the Instructor Guide.
- Ask participants to identify all safety problems indicated in the story.
- Discuss how the worker could have handled the situation in a better manner.
Discuss any points from "Maintenance Precautions" and "Driving in Traffic" that haven't been mentioned.
Discussion
What is the company's policy for ventilating the repair shop while working on equipment with the engine running?
Hands-on Exercises
- Ask participants to inspect an aerial lift using a checklist such as the Pre-Start Checklist on page 10 of the Aerial Lift Safety manual or the Pre-Operation Inspection provided on page 199 of the Instructor Guide. After the inspection, ask participants to identify crush points and discuss appropriate precautions.
- With the class observing, ask a participant to demonstrate how to safely fuel an aerial lift. Why is it important to touch the fuel nozzle to the lift before opening the fuel cap?
- Have the class set up an aerial lift for operation in safe area. Individually, have participants start the aerial lift, operate the basic controls, and shut it down. Before beginning, instruct participants about the operating controls and keep everyone out of the way. Discuss any procedures that may be relevant for other types of aerial lifts. Practice attaching and operating any attachments employees will be expected to use.
- In a safe area such as a private road or parking lot on your company's property, have participants set up a roadside work area using traffic cones and flaggers, as appropriate. Make sure all participants wear brightly-colored reflective vests and any other safety equipment that your organization requires for this type of work. Guidelines for roadside work areas are detailed in the Motor Vehicle Safety Manual for Landscaping and Horticultural Services http://www.oznet.ksu.edu/agsafe/training/OSHA_training.htm
Evaluation
Answer the quiz items on page 13 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual either individually or as a class. Be sure to discuss each item.
Lesson 3 Prevent Lift Overturns
Suggested Objectives
- Identify safe operating procedures to prevent a lift overturn.
Discuss the Accident Reports on pages 14 -15 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual
Case Studies
Break the class into small groups of three to five participants. Provide each group with one of the scenarios on pages 182-184 of this Instructor Guide. Ask each group to discuss their scenario, using the information from Lesson 3 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual. If there are more than three groups, more than one group can work on the same scenario. Monitor the progress of each group. Bring the class back together and ask for a representative from each group to read their problem and explain their solution. Display case study overheads as each group takes turns. Ask other groups what they think of the proposed solution.
Hands-on Exercise
Break the class into groups of three to five participants. Identify several distinct tree-trimming areas nearby. Have each group evaluate a work area for hazards that could result in an overturn. Bring the class back together and have each group report about the hazards they observed and precautions that need to be taken.
Evaluation
Answer the quiz items on page 16 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual either individually or as a class. Be sure to discuss each item.
Lesson 4 Prevent Falls from Aerial Lifts
Suggested Objectives
- Identify steps to secure yourself in the bucket of the lift.
- Recognize safe operating procedures to avoid falling from an aerial lift.
- Indicate how to avoid being struck by objects that fall from the lift.
Discuss the Accident Reports on pages 17 -18 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual
Case Studies
Break the class into small groups of three to five participants. Provide each group with one of the scenarios on pages 185-187 of this Instructor Guide. Ask each group to discuss their scenario, using the information from Lesson 4 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual. If there are more than three groups, more than one group can work on the same scenario. Monitor the progress of each group. Bring the class back together and ask for a representative from each group to read their problem and explain their solution. Display case study overheads as each group takes turns. Ask other groups what they think of the proposed solution.
Hands-on Exercise
- Have participants perform an inspection of a lanyard, harness and any other fall protection equipment they will be using.
- Demonstrate and ask participants to practice securing themselves in the lift bucket with the fall protection equipment they will be using.
Evaluation
Answer the quiz items on page 19 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual either individually or as a class. Be sure to discuss each item.
Question/Discussion
Before beginning Lesson 5:
- Ask participants if it is possible to get electrocuted by a power line if they don't actually touch the line. What are some ways this can happen? List responses on an overhead or flipchart.
- Are participants aware that most power lines are not insulated?
- Have participants known of anyone who has been electrocuted from a power line? Would they care to share what happened?
Lesson 5 Avoid Contact With Power Lines
Suggested Objectives
- Differentiate between qualified and unqualified line-clearance tree trimmers.
- Recognize electrical hazards.
- Identify safe working distances from power lines.
Discuss the Accident Reports on pages 20 -21 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual
- Discuss how participants could be electrocuted without actually touching a power line. How well does this information match the list they made earlier? Are they surprised by any of the differences?
- Regarding work around power lines, what is the difference between qualified and unqualified employees? Have any of the participants had the additional training needed to become qualified?
- Discuss your company's policy regarding work around power lines. What is the procedure for contacting the electric company when power lines need to be shut down or shielded?
- Discuss what participants would do if their aerial lift came in contact with a power line.
- Discuss your company's policy regarding workers on the ground when a lift is being used to trim trees near power lines.
- Discuss insulation features and grounding requirements of the company's lift trucks. What are the limitations of these features? What are the operator's responsibilities for checking these features before each job?
Hands-on Exercise
- As a group, go outside and evaluate hazards involving nearby trees. For qualified and unqualified employees, what precautions need to be taken before trimming specific trees?
Evaluation
Answer the quiz items on page 23 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual either individually or as a group. Be sure to discuss each item.
Lesson 6 Environmental Hazards
Suggested Objectives
- Identify environmental hazards.
- Recognize treatment and first aid for exposure to environmental hazards.
Case Studies
Break the class into small groups of three to five participants. Provide each group with one of the scenarios on pages 188-190 of this Instructor Guide. Ask each group to discuss their scenario, using the information from Lesson 6 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual. If there are more than three groups, more than one group can work on the same scenario. Monitor the progress of each group. Bring the class back together and ask for a representative from each group to read their problem and explain their solution. Display case study overheads as each group takes turns. Ask other groups what they think of the proposed solution.
Discuss
- When you are using an aerial lift in frigid winter weather, what body parts are most likely to be injured by the cold? Why?
- Ask participants what actions they have found most effective for preventing cold-induced injury.
- Have any participants ever had a bad experience with insects, animals, or poisonous plants while working at their jobs? Would they care to share what happened?
Hands-on Exercise
Using the company's first aid kits, demonstrate and have participants practice first aid for cuts, burns, heat exhaustion, cold injury and lightning strike.
Evaluation
Answer the quiz items on page 30 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual either individually or as a class. Be sure to discuss each item.
Conclusion
Contest
Divide the class into groups. Display the contest items provided on pages 191-197 of the Instructor Guide. In turn, ask each group a multiple choice or true/false question from the overheads. Each group gets one point for every correct answer. If a group misses a question, allow the next group to answer it for a point. Keep track of points and recognize the winning group. Use the questions as opportunities to discuss the training material. Answer key provided on page 198 of the Instructor Guide.
Discussion
Ask participants to share any questions or concerns they may still have or want to discuss further.
Evaluation
Answer the quiz questions on pages 32-33 of the Aerial Lift Safety Manual individually or as a group. Be sure to discuss each item.
Hands-on Performance Evaluation
In a safe area with adequate supervision, have each participant complete a hands-on performance evaluation while operating an aerial lift in small "work crews". The evaluation may include:
- Pre-Operation Inspection provided on page 199 of the Instructor Guide
- Determining if power line precautions are required
- Setting up the lift
- Maneuvering
- Safe shut-down
A checklist for the performance evaluation is provided on page 200 of the Instructor Guide.
Visual Aid (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 2)
Is This a Good Idea?
A worker was getting an aerial lift truck ready for work. With the engine running, he raised the boom and then stood underneath it while he greased the lubrication points. He lowered the boom, used a bumper jack to raise the front of the truck, and crawled underneath to change the oil. When he finished, he tossed his tools in the bucket of the boom, hopped in the cab, and headed for the job site.
Case Study # 1 ((Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 3)
You have been asked to use the boom of your aerial lift to pick up some logs and set them in the back of a dump truck. What issues do you need to consider? What precautions should you take to avoid an overturn?
Case Study # 2 (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 3)
A few hours after a severe thunderstorm, your crew is sent to trim damaged trees in a residential area with an aerial lift. You have never been to this area before. In regard to rollovers, what hazards or problems do you anticipate? How will you protect yourself and your crew?
Case Study # 3 (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 3)
You have been assigned to trim trees with an aerial lift along a power line next to a rural two-lane highway. You have never been assigned to this area before. In regard to rollovers, what hazards or problems do you anticipate? How will you protect yourself and your crew?
Case Study # 1 (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 4)
You have been assigned to trim trees in a new area. You have been told the trees are "hard to reach." In regard to falling from the lift, what problems do you anticipate? How will you protect yourself?
Case Study # 2 (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 4)
You have been assigned to trim trees on a day when there is a chance of gusty winds. In regard to falling from the lift, what problems do you anticipate? How will you protect yourself?
Case Study # 3 (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 4)
You are in charge of a work crew that is trimming storm-damaged trees in a residential area. How will you protect your crew and residents from falling limbs while you work?
Case Study # 1 (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 6)
Your crew is heading out for what you expect to be a long, hard day. The forecast calls for hot and humid weather. One of your crew members is new, and has been working less than a week. What issues do you need to consider and what precaution should you take to protect the crew from the heat and sun?
Case Study # 2 (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 6)
Your crew has been working hard all day. The weather is hot and sunny. A crew member says he feels ill. His skin is pale and sweaty and he is sick to his stomach.
- What actions do you take?
- Despite your efforts, your crew member begins acting disoriented. His skin turns red, hot and dry. Now what actions do you take?
Case Study # 3 (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Lesson 6)
You are trimming isolated trees next to a power line in a lakeside picnic area. The sky looks stormy and dark. You think you see a flash of lightning on the horizon, but you can't hear any thunder.
- What actions do you take?
- Suddenly, lightning flashes nearby. You have your aerial lift truck. There is also an open shelter house and a dry culvert under the road. Now what actions do you take?
Contest (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Conclusion)
- Which of the following is the most serious safety message?
- Danger
- Warning
- Caution
- You are required to use a lanyard and a body belt or harness when working in the bucket of an aerial lift.
True/False
- Which is the best practice when setting up an aerial lift at a job site?
- Use outriggers and make sure the lift is stable.
- Set up the lift on soft, muddy ground.
- If your lift is insulated, cover the surface of the boom with a light coating of grease.
- Do not perform maintenance beneath a raised boom unless it is supported by:
- a concrete block.
- an approved support device.
- a jack.
- Which of the following practices is the safest for a worker in the bucket?
- If the boom acts sluggish, try popping and jerking the controls.
- The operator on the ground should get permission from the worker in the bucket before using the lower controls.
- When it is windy, the worker in the bucket should attach one end of the lanyard to the safety belt and the other to a nearby tree or pole.
- Which of the following will help you avoid overturning the lift?
- Park away from the work and reach as far as possible with the boom.
- Operate the lift controls as rapidly as possible.
- Completely lower and secure the boom before moving the truck
- Which is the best practice when lifting a load?
- Check the operator's manual for lifting capacity and procedures.
- Position a worker under the load to give hand signals to the operator.
- Once the load is in the air, swing it rapidly into position
- You need to trim a high branch, but the lift will not reach. Which of the following is safer?
- Set up a ladder in the bucket.
- Use a pole saw while standing on the floor of the bucket.
- Attach your lanyard to the tree and stand on top of the bucket.
- Which is the best practice when cutting limbs?
- The worker in the bucket should drop limbs to workers waiting on the ground.
- The worker in the bucket should lower limbs by hand to workers on the ground.
- Workers on the ground should stay away while the boom is raised.
- Workers must keep their distance from energized power lines. How far away must an unqualified worker be at all times?
- At least 3 feet, depending on voltage.
- At least 7 feet, depending on voltage.
- At least 10 feet, depending on voltage.
- Which of the following is the best practice when working around power lines?
- Keep enough distance to allow for sway of the boom and lines.
- Drill extra holes in the bucket to reduce the wind resistance.
- Make sure workers on the ground stand close to the lift.
- Prevent skin cancer by covering exposed skin with a broad spectrum sunscreen that has a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of at least:
- 5
- 10
- 15
- When working in the heat, how much water should you drink to avoid heat illness?
- 1 cup per hour.
- 1 quart per hour.
- 1 gallon per hour.
- Use _____________ to stop bleeding from minor cuts.
- a tourniquet
- direct pressure
- warm water
- When a worker is elevated in the bucket, the lower controls should only be used with the permission of the elevated worker or in case of an emergency.
True/False
Contest Answer Key (Aerial LIft Truck Safety Conclusion)
- a
- T
- a
- b
- b
- c
- a
- b
- c
- c
- a
- c
- b
- b
- T
Forms (PDF)
Daily Pre-Operation Inspection: Aerial Lift
Operator Performance Evaluation: Aerial Lift
Publication #: MF2716
This material was produced under grant number 46G3-HT04 from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U.S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. government.
This booklet was produced by K-State Research and Extension, Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas.
The information in this publication has been compiled from a variety of sources believed to be reliable and to represent the best current opinion on the subject. However, neither K-State Research and Extension nor its authors guarantee accuracy or completeness of any information contained in this publication, and neither K-State Research and Extension or its authors shall be responsible for any errors, omissions, or damages arising out of the use of this information. Additional safety measures may be required under particular circumstances.
Brand names appearing in this publication are for product identification purposes only. No endorsement is intended, nor is criticism implied of similar products not mentioned.
Disclaimer and Reproduction Information: Information in
NASD does not represent NIOSH policy. Information included in
NASD appears by permission of the author and/or copyright holder.
More