Introduction
What's Inside?.
Training Techniques.
Tractor Safety Training Guide.
Motor Vehicle Safety Training Guide.
Chipper/Shredder Safety Training Guide.
Skid Steer Safety Training Guide.
Tree Trimming Safety Training Guide.
Aerial Lift Safety Training Guide.
Mowing and Trimming Safety Training Guide.
Suggested Materials
Sources of Background Information
Skid Steer and Motor Vehicle Safety Training Manuals available for download: http://www.oznet.ksu.edu/library/Landscaping_Equipment_Safety.htm
Operator's manuals for skid steer loaders (available from dealer)
Length of Time Needed for Training
Review and select the learning activities that are most appropriate. If all of the discussion and hands-on exercises are included in the training it may take up to a full work day. Without the hands-on exercises, the classroom portion will take about two hours.
Welcome and Introduction
Participant Introductions
Find out:
Questioning/Discussion
Before beginning Lesson 1:
Discuss Accident Reports on pages 4 -5 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual
Discussion Items
Discuss the Safety Signs on page 6 of the Chipper/Shredder Safety Manual
Visual Aid
Discuss the Safety Signs on page 6 of the Skid Steer Loader Manual
Can participants recall any safety signs they have seen on equipment?
Evaluation
As a group, answer the quiz items on page 7 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual. Be sure to discuss each item.
Questioning/Discussion
Before beginning Lesson 2:
Discuss the Pre-Start Inspection information and Checklist on page 8 -9 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual
Discussion Items
Analysis
Ask participants to silently read "Safe Start and Shut Down" on pages 9-11 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual. For each numbered or bulleted item, ask participants to write a "C" in the margin if the item mainly protects them from being crushed by moving parts. Write an "R" in the margin if the items mainly addresses being run over. Write a "B" in the margin if the item mainly addresses both of these hazards. Write an "O" in the margin if the item mainly addresses other hazards. When everyone has finished, have each participant read an item and briefly tell what type of accident it will prevent and why. Be sure to discuss items that participants find surprising or difficult to comply with.
Discuss the Accident Reports on pages 10-11 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual
Evaluation
Individually or as a group, answer the quiz items on page 12 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual. Be sure to discuss each item.
Hands-on Exercise
Suggested Objectives
Discuss the Accident Reports on pages 13 -14 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual
Case Studies
Break the class into small groups of three to five participants. Provide each group with one of the scenarios on pages 122-125 of this Instructor Guide. Ask each group to discuss their scenario, using the information from Lesson 3 of the Skid Steer Safety Manual. If there are more than four groups, more than one group can work on the same scenario. Monitor the progress of each group. Bring the class back together and ask for a representative from each group to read their problem and explain their solution. Display case study overheads as each group takes turns. Ask other groups what they think of the proposed solution.
Hands-on Exercise
Show the class one or more skid steer loaders (parked and properly shut down). Ask participants to point out locations where they could be crushed by moving parts while operating the loader. Locate data plates and load capacities for the skid steer loader(s). Demonstrate the proper use of the safety belt and bar.
Evaluation
Answer the quiz items on page 16 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual. Be sure to discuss each item.
Discuss the Accident Reports on pages 17 -19 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual
Discussion
Case Studies
Break the class into small groups of three to five participants. Provide each group with one of the scenarios on pages 126-128 of this Instructor Guide. Ask each group to discuss their scenario, using the information from Lesson 4 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual. If there are more than three groups, more than one group can work on the same scenario. Monitor the progress of each group. Bring the class back together and ask for a representative from each group to read their problem and explain their solution. Display case study overheads as each group takes turns. Ask other groups what they think of the proposed solution.
Visual Aid
Display and discuss the overheads of skid steer loaders on pages 129-134. Ask participants to identify the safer way to operate the skid steer loader to avoid a rollover. Answer key provided on page 135.
Evaluation
As a group, answer the quiz items on page 21 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual. Be sure to discuss each item.
Discuss the Accident Report on page 22 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual
Discussion Items
Discuss the Accident Report on page 23 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual
Discuss the Accident Report on page 23 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual
Evaluation
Answer the quiz items on page 26 of the Skid Steer Safety Manual either individually or as a class. Be sure to discuss each item.
Hands-on Exercise
Case Studies
Break the class into small groups of three to five participants. Provide each group with one of the scenarios on pages 136-138 of this Instructor Guide. Ask each group to discuss their scenario, using the information from Lesson 6 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual. If there are more than three groups, more than one group can work on the same scenario. Monitor the progress of each group. Bring the class back together and ask for a representative from each group to read their problem and explain their solution. Display case study overheads as each group takes turns. Ask other groups what they think of the proposed solution.
Discussion
Discussion
Evaluation
Answer the quiz items on page 33 of the Skid Steer Loader Safety Manual either individually or as a class. Be sure to discuss each item.
Hands-on Exercise
Using your company's first aid kits, demonstrate and have participants practice first aid for common injuries such as cuts and burns.
Contest
Divide the class into groups. Display the contest items provided on pages 139-145 of the Instructor Guide. In turn, ask each group a multiple choice or true/false question from the overheads. Each group gets one point for every correct answer. If a group misses a question, allow the next group to answer it for a point. Keep track of points and recognize the winning group. Use the questions as opportunities to discuss the training material. Answer key provided on page 146 of the Instructor Guide.
Discussion
Ask participants to share any questions or concerns they may still have or want to discuss further.
Evaluation
Answer the quiz questions on page 35 individually or as a group. Be sure to discuss each item.
Hands-on Performance Evaluation
In a safe area with adequate supervision, have each participant complete a hands-on performance evaluation while operating a skid steer loader (including attachments, if appropriate). The evaluation may include completing:
A checklist for the performance evaluation is provided on page 121 of the Instructor Guide.
Visual Aid (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 1)
Deaths Involving Skid Steer Loaders |
|
59% = |
Pinned/crushed between bucket and frame or between lift arms and frame |
19% = |
Rollover |
16% = |
Crushing incidents with no further information provided |
2% = |
Pinned/crushed between loader and another object |
1% = |
Run over |
2% = |
Other/Unknown |
| Composite results of government studies involving a total of 1 deaths reported in National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Publication Number 98 -117 | |
Case Study # 1 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 3)
You are using an older skid steer loader with a front bucket attachment. While lifting a load, the lift arms get stuck in the raised position. One of your coworkers sees that you are having a problem and comes to help. What precautions should be taken regarding: getting safely out of the loader? keeping your coworker safe? repairing the loader?
Case Study # 2 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 3)
You are using a loader with a bucket attachment to move dirt around a building foundation. There are lots of trees and shrubs near the foundation, so you are placing the dirt as close as you can, while coworkers on the ground are spreading the dirt with shovels. What issues do you need to consider and what precautions should you take to protect your coworkers?
Case Study # 3 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 3)
Your boss sends you to get the skid steer loader. When you get to the equipment shed, you find that someone has been using the loader and didn't shut it down properly. The engine is running, the lift arms and bucket are raised, but you don't see anyone around. What issues do you need to consider and what precautions should you take in order to safely enter and move the loader?
Case Study # 4 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 3)
It is winter, and you will be using the skid steer loader. Upon inspection, you see that ice and frozen mud have accumulated under the front of the loader. You believe the loader will be damaged if you try to operate it without first clearing away the ice and mud. The only way to clean the loader is to raise the lift arms and then work underneath. Describe how you will plan this job to make sure no one gets hurt while cleaning under the front of the loader.
Case Study # 1 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4)
You are using a skid steer loader to load trucks with soil and other materials. The soil is stored outside, but some materials are stored in a warehouse. A ramp leads to a raised dock where you will load the trucks. Most of the floor is concrete, but a part is older wood. What issues do you need to consider and what precautions should you take to avoid a rollover accident? What precautions should you take to protect your coworkers?
Case Study # 2 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4)
You are assigned to use a skid steer loader to move logs and brush where trees were recently felled on a hillside. For the most part, the hill has a very gentle slope, but there are a few steep gullies and some uneven ground. Some of the logs are very small, while others are quite large. What issues do you need do consider and what precautions should you take to avoid rollover accidents while operating here?
Case Study # 3 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4)
You need to use a skid steer loader with a fork attachment to unload bundles of landscape timbers from a tractor-trailer. You will be moving the timbers to raised storage racks in a crowded warehouse. There is no loading dock, so the tractor trailer has to be unloaded from the ground on the gravel parking lot. What issues do you need to consider and what precautions should you take to avoid rollover accidents while operating here?
Visual Aid (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4)Which is Safer? |
| Driving on a hill with an empty bucket |
 |
 |
Visual Aid (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4)Which is Safer? |
| Driving on a hill with a heavy load in the bucket. |
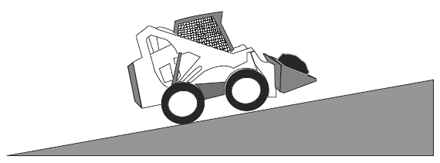 |
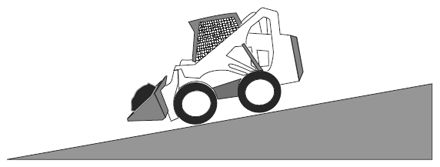 |
Visual Aid (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4)Which is Safer? |
| Driving forward with a heavy load in the bucket. |
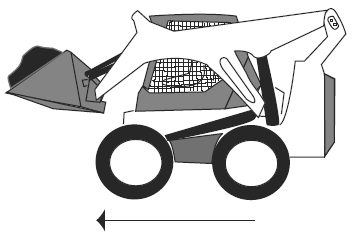 |
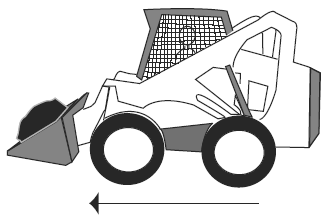 |
| Visual Aid (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4) Which is Safer? |
| Driving on a hill with an empty bucket |
 |
 |
Visual Aid (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4)Which is Safer? |
| Driving on a hill. |
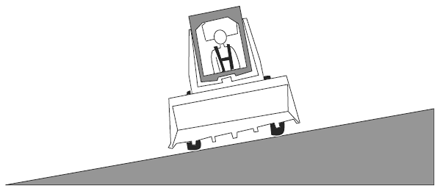 |
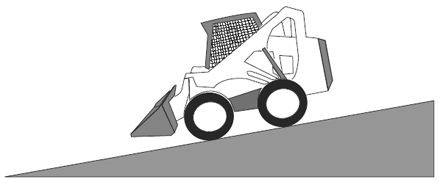 |
| Visual Aid (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4) Which is Safer? |
| Driving with a large log in the bucket. |
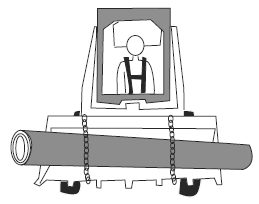 |
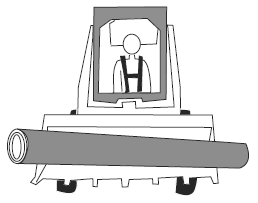 |
Visual Aid (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4)Which is Safer? |
| Carrying a heavy object. |
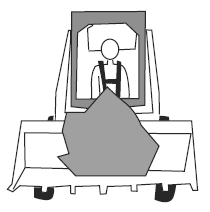 |
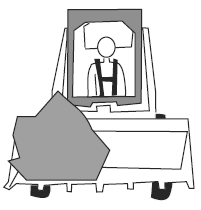 |
| Visual Aids Answer Key (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 4) |
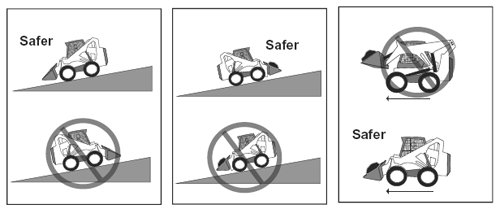 |
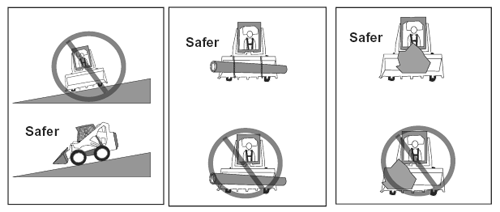 |
Case Study # 1 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 6)
Your crew will be working in large open area tomorrow (no shade). The weather is expected to be very hot and humid. One of your crew members is new, and it will be his first day on the job. What issues do you need to consider and what precautions should you take to protect the crew from heat illness?
Case Study # 2 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 6)
You and another worker have been working all day. The weather is hot and sunny. You notice your coworker doesn't look good. His skin is pale and sweaty and he says he feels sick to his stomach.
Case Study # 2 (Skid Steer Loader Safety Lesson 6)
You are clearing trees and brush along a powerline in a rural area. There is a severe thunderstorm watch in effect, and the sky looks stormy and dark. You think you see a flash of lightning far off on the horizon. You listen for thunder, but you don't hear anything other than the wind.
Contest (Skid Steer Loader Safety Conclusion)
Contest Answer Key (Skid Steer Loader Safety Conclusion)
Forms (PDF)
Daily Pre-Operation Inspection: Skid Steer Loader
Evaluation/Performance Checklist: Skid Steer Loader
Publication #: MF2716
This material was produced under grant number 46G3-HT04 from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U.S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. government.
This booklet was produced by K-State Research and Extension, Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas.
The information in this publication has been compiled from a variety of sources believed to be reliable and to represent the best current opinion on the subject. However, neither K-State Research and Extension nor its authors guarantee accuracy or completeness of any information contained in this publication, and neither K-State Research and Extension or its authors shall be responsible for any errors, omissions, or damages arising out of the use of this information. Additional safety measures may be required under particular circumstances.
Brand names appearing in this publication are for product identification purposes only. No endorsement is intended, nor is criticism implied of similar products not mentioned.
Disclaimer and Reproduction Information: Information in NASD does not represent NIOSH policy. Information included in NASD appears by permission of the author and/or copyright holder. More